cADDis: Live Cell Assays for cAMP
Detect Gs or Gi signaling with cADDis, our cAMP Assay
- Use cADDis to measure cAMP through Gs or Gi signaling in real time with a single sensor
- Plate reader or imaging system compatible
Measure cAMP through Gs or Gi Signaling in Real Time with a Single Sensor
- Quantify kinetics of cyclic AMP signaling in living cells.
- Measure cAMP for many hours with minimal loss of sensor signal.
- Robust expression in practically any cell type.
cADDis cAMP Assays
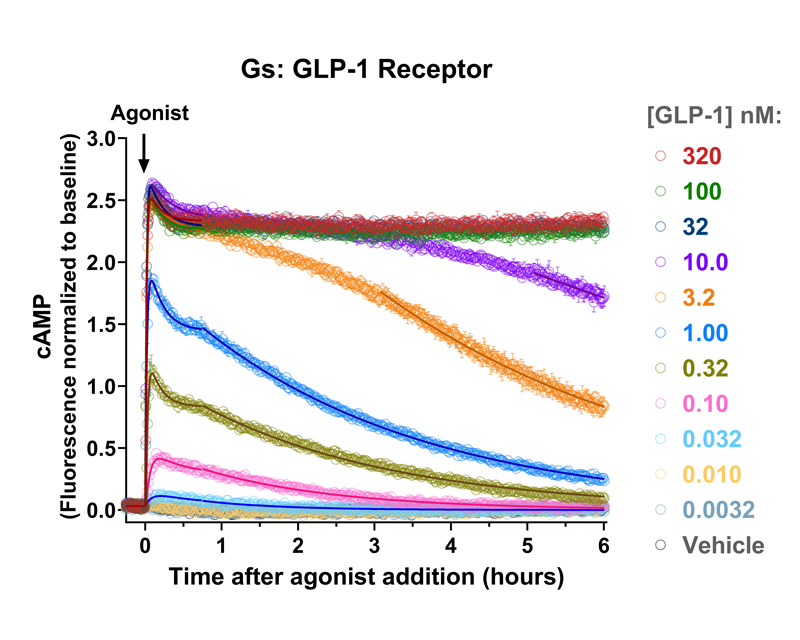
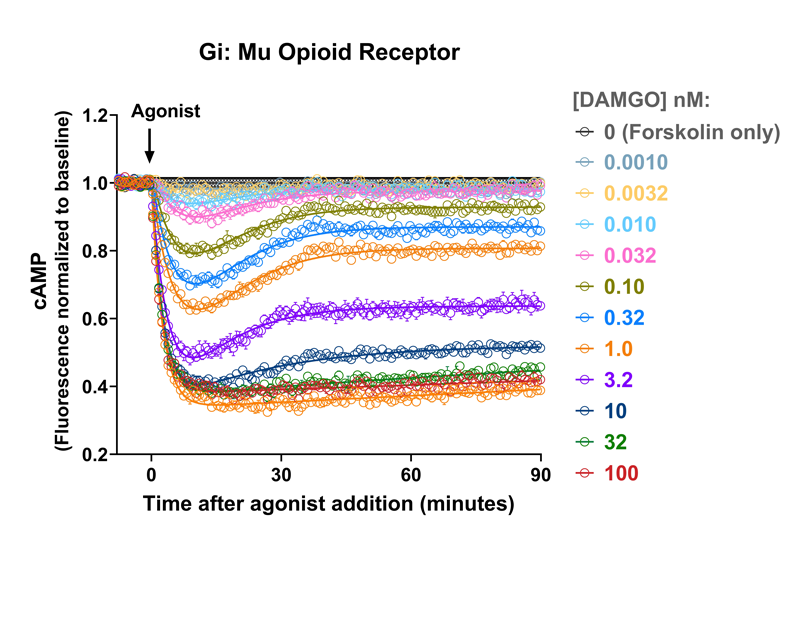
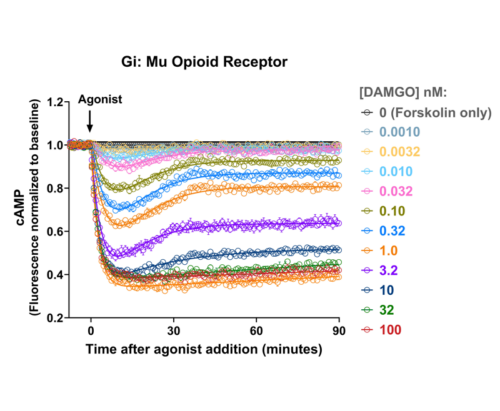
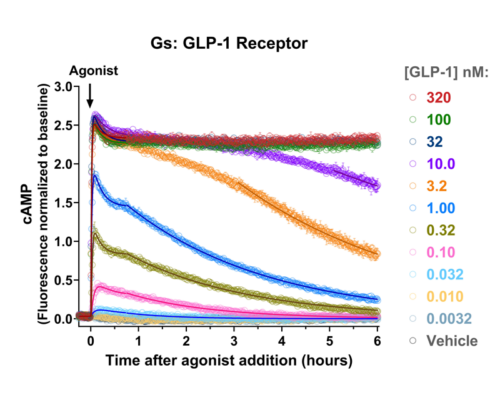
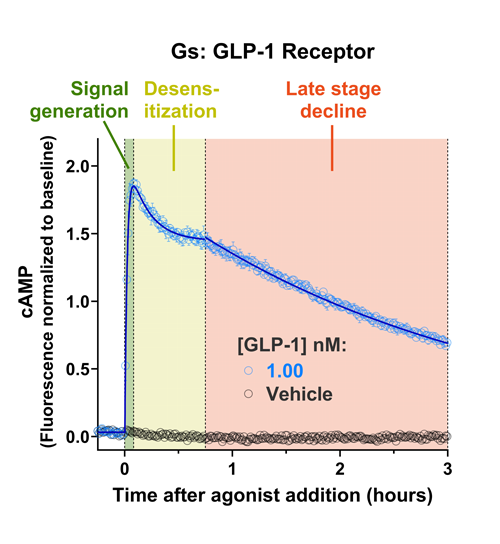
Quantify cAMP Kinetics Precisely
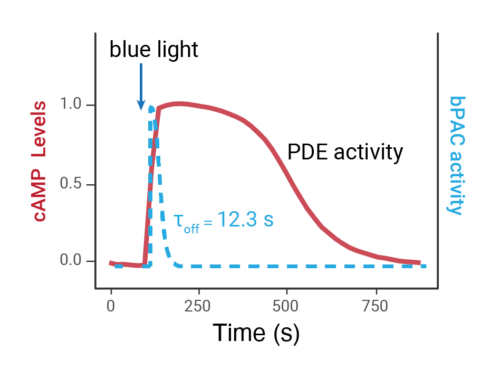
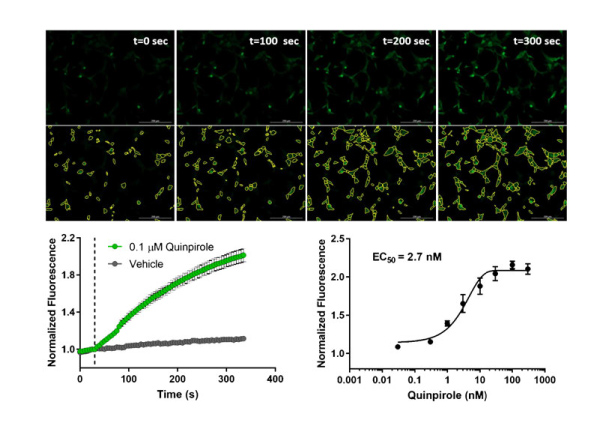
- Changes over time reflect biological signaling mechanisms (rather than technical artifacts like sensor decay).
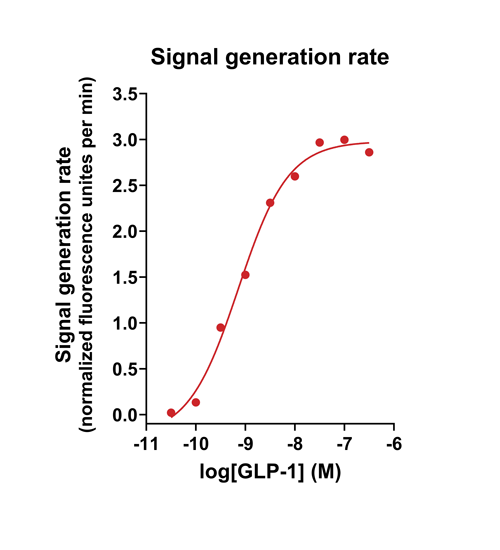
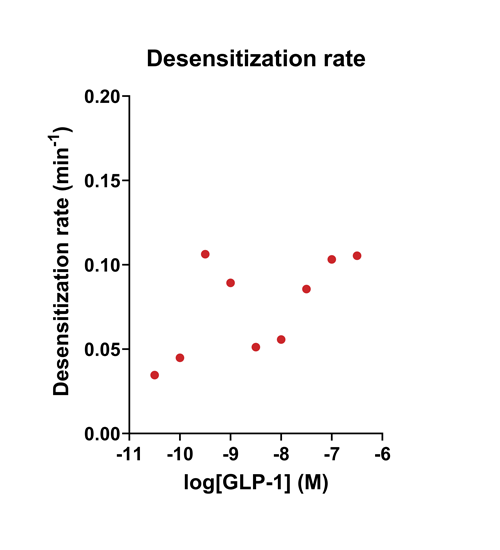
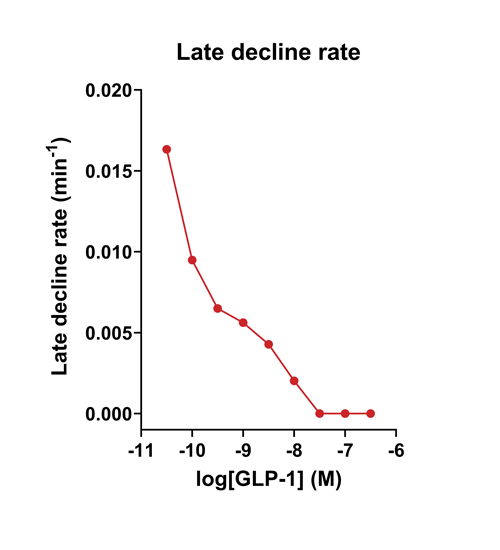
- Quantify signaling mechanisms by curve fitting time course data (see here for example report).
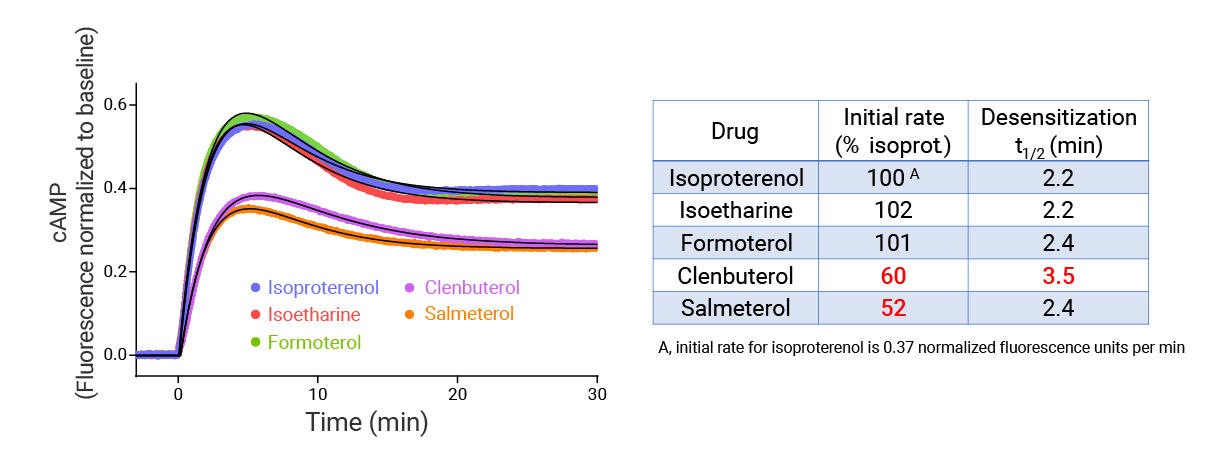
- In the example below we quantify the signal generation rate, signal decline resulting from desensitization, and late stage decline (likely resulting from peptide ligand degradation).
Your endpoint assays are missing important information. Measuring kinetics with our live-cell assays can reveal it.
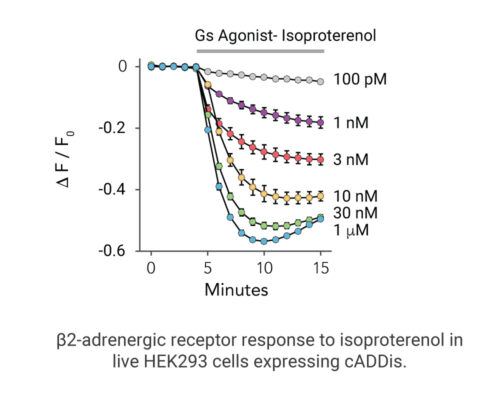
- Signaling dynamics of multiple drug compounds
- Different dynamics of cAMP generation by β2 adrenergic receptor agonists
- Clenbuterol and salbutamol generate cAMP more slowly and clenbuterol desensitizes receptor more slowly
A Robust & Versatile cAMP Assay Kit
- cADDis is a genetically-encoded fluorescent cyclic AMP assay that detects changes in cAMP in real time. Off the shelf kits include the cADDis sensor in BacMam, a BSL-1 viral vector for efficient delivery to most cell types. Purified BacMam, AAV, Lenti vectors by request.
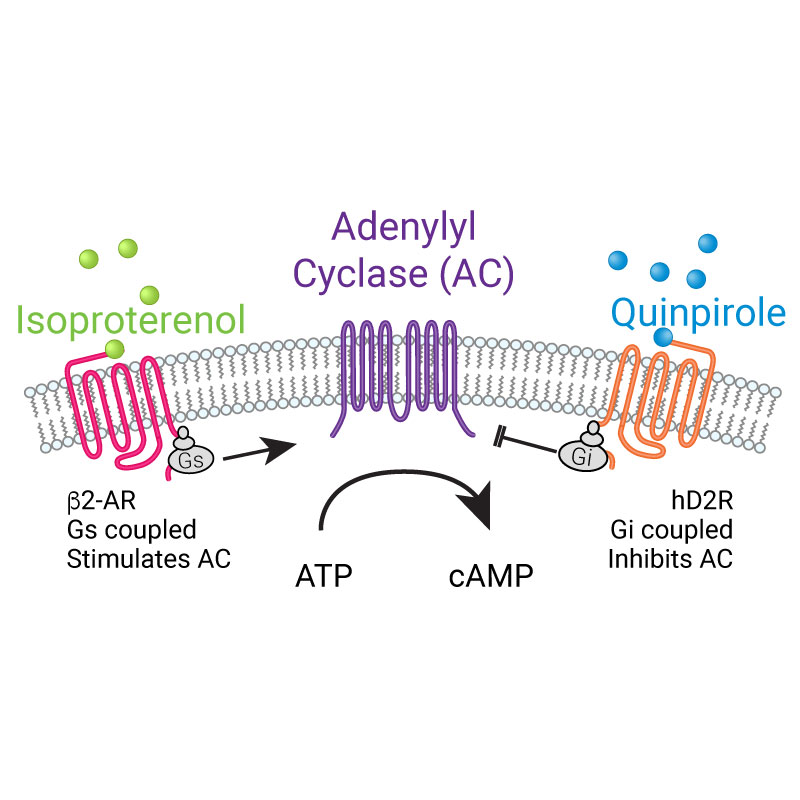
- Screen Gs or Gi-coupled GPCRs in living cells
- Target to microdomains or specific cells in mixed cultures
- Robust expression in practically any cell type
- Easily detectable on plate readers or imaging systems
- Controllable expression in BacMam viral vector
- High signal-to-noise ratio
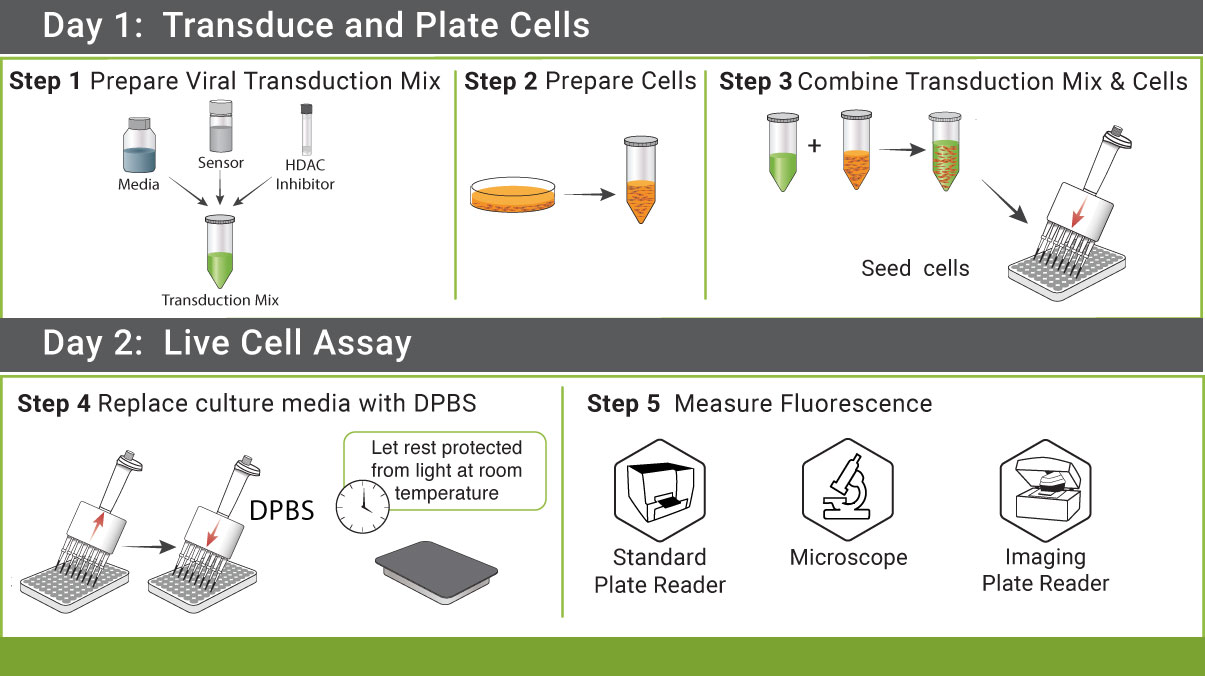
Simple Protocol
GPCR Assay Services
Go from hit to lead faster with compound profiling assays that capture GPCR signaling dynamics in living cells. Our unique biosensor-based discovery platform quantifies multiple signaling parameters in real time to enable decisions based on clinically-relevant data. Our fast turnaround time helps reduce the time to the clinic. We will perform experiments to advance your projects and programs, for example by optimizing assays, profiling compounds, exploring mechanisms and kinetically characterizing signaling dynamics.
Check out this Application Note from BioTek Instruments: Characterizing Gs- and Gi-Dependent Regulation of cAMP Levels in Real Time with cADDis Biosensor and Automated Live‑Cell Imaging
Recent Publications
- Mark Lee & Keren Hilgendorf. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits adipogenesis through the cilia-dependent activation of ROCK2. Journal of Cell Science. September 2025.
- R. Nassini, et al. Targeting prostaglandin E2 receptor 2 in Schwann cells inhibits inflammatory pain but not inflammation. Nature Communications. September 2025.
- Tatsuru Togo. Disruption of the cell membrane triggers Ca2+ mobilization using P2Y receptors and subsequent cAMP synthesis in cells surrounding wounded MDCK cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. September 2025.
- C. Sturaro, et al. Activation of peripheral NOP receptors reduces periorbital mechanical allodynia evoked by CGRP in mice. British Journal of Pharmacology. August 2025.
- T. Cacciottolo, et al. Glucagon Receptor Deficiency Causes Early-Onset Hepatic Steatosis. Diabetes. August 2025.
- J. Chadwick, et al. Dietary-dependent sensitization of neuronal leptin signaling promotes neural repair after injury via cAMP and gene transcription. Neuron. August 2025.
- K. Berger, et al. Design of a peripherally biased NPSR1 antagonist for neuropeptide S induced inflammation. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. August 2025.
- C. Gao, et al. Semaglutide drives weight loss through cAMP-dependent mechanisms in GLP1R-expressing hindbrain neurons. bioRxiv. August 2025.
- Y. Manchanda, et al. Glycaemic and bodyweight effects of GIPR coding variation reflect differences in both surface expression and intrinsic functional impairment. medRxiv. August 2025.
- S. Orfanos, et al. The differential effects of cAMP mobilizing agents on TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix in human lung-derived fibroblasts: Insights into therapeutic targets for lung fibrosis. Research Square. August 2025.
- N. Saito, et al. Activation of G protein-coupled parathyroid hormone receptors in rat incisor odontoblasts promotes mineralization via cyclic adenosine monophosphate, not Ca2+ signalling: In vitro study. International Endodontic Journal. July 2025.
- M. Merz, et al. Downstream Signaling of Muscarinic M4 Receptors Is Regulated by Receptor Density and Cellular Environment. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives. May 2025.
- B. Wysolmerski, et al. Conformational biosensors delineate endosomal G protein regulation by GPCRs. bioRxiv. May 2025.
- Paul G. DeCaen & Louise F. Kimura. Methods to Assess Neuronal Primary Cilia Electrochemical Signaling. Journal of Cellular Physiology. April 2025.
- A. Oqua, et al. Molecular mapping and functional validation of GLP-1R cholesterol binding sites in pancreatic beta cells. eLife. April 2025. (bioRxiv)
- L. Coassolo, et al. Prohormone cleavage prediction uncovers a non-incretin anti-obesity peptide. Nature. March 2025.
- R. Schuck, et al. Cholesterol inhibits assembly and oncogenic activation of the EphA2 receptor. Nature Communications Biology. March 2025.
- E. Blythe, et al. Endocytosis sculpts distinct cAMP signal transduction by endogenously coexpressed GPCRs. bioRxiv preprint. February 2025.
- S. Orfanos, et al. The differential effects of cAMP mobilizing agents on inhibition of TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix and growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts. Authorea. February 2025.
- A. Klein, et al. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase 1 (AC1) and exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) restores ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel activity after chronic opioid exposure. bioRxiv. February 2025.
- I. Davies, et al. Chronic GIPR agonism results in pancreatic islet GIPR functional desensitisation. Molecular Metabolism. January 2025.
- N. Patel, et al. Myosin VI drives arrestin-independent internalization and signaling of GPCRs. Nature Communications. December 2024.
- C. Bonner, et al. Metabolic State Determines Central and Peripheral Mechanisms of Liraglutide-Enhanced Insulin Secretion. Research Square. December 2024.
- M. Kimura, et al. Intracellular cAMP signaling-induced Ca2+ influx mediated by calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) in human odontoblasts. European Journal of Physiology. November 2024.
- A. Ali, et al. Comparative Effects of GLP-1 and GLP-2 on Beta-Cell Function, Glucose Homeostasis and Appetite Regulation. Biomolecules. November 2024.
Posters: cADDis cAMP Assay
Measuring long term GPCR signaling and arrestin recruitment using fluorescent biosensors
GLP-1, glucagon and GIP receptor signaling dynamics were quantified using fluorescent cAMP and arrestin recruitment biosensors, identifying major differences of the duration of signaling between receptors, and between different agonists activating the GLP-1 receptor.
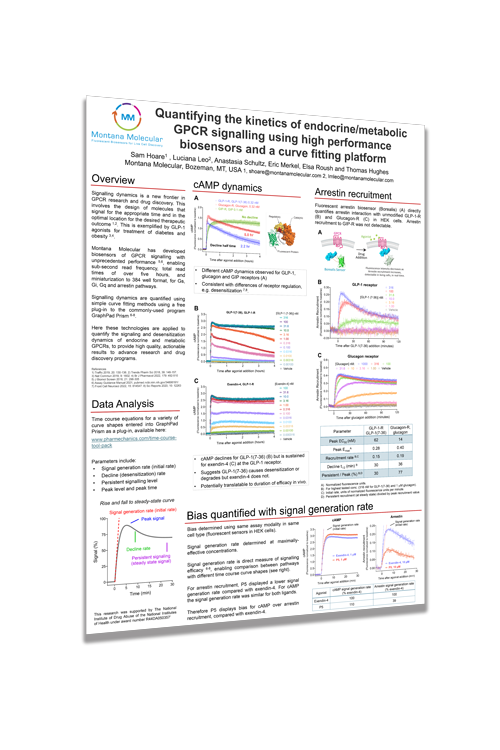
Quantifying the kinetics of endocrine/metabolic GPCR signalling using high performance biosensors and a curve fitting platform
Montana Molecular has developed biosensors of GPCR signaling with unprecedented performance, enabling sub-second read frequency, total read times of over five hours, and miniaturization to 384-well format, for Gs, Gi, Gq and arrestin pathways. Signaling dynamics are quantified using simple curve fitting methods using a free plug-in to the commonly-used program GraphPad Prism. Here these technologies are applied to quantify the signaling and desensitization dynamics of endocrine and metabolic GPCRs, to provide high quality, actionable results to advance research and drug discovery programs.
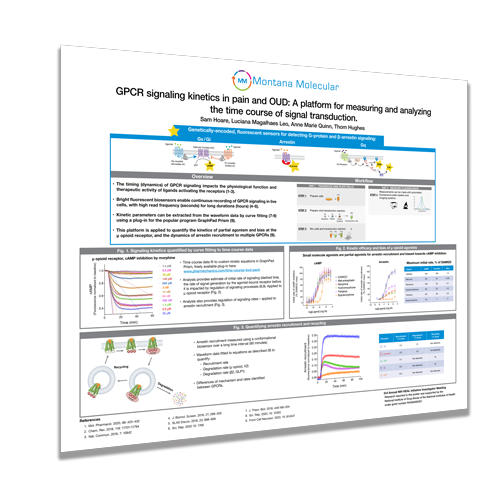
GPCR signaling kinetics in pain and OUD: A platform for measuring and analyzing the time course of signal transduction
- The timing (dynamics) of GPCR signaling impacts the physiological function and therapeutic activity of ligands activating the receptors.
- Bright fluorescent biosensors enable continuous recording of GPCR signaling in live cells, with high read frequency (seconds) for long durations (hours)
- Kinetic parameters can be extracted from the waveform data by curve fitting using a plug-in for the popular program GraphPad Prism
- This platform is applied to quantify the kinetics of partial agonism and bias at the μ-opioid receptor, and the dynamics of arrestin recruitment to multiple GPCRs.
GPCR Biology
Increase your understanding of drug effects and GPCR biology with bright fluorescent assays for Gs, Gi, and Gq signaling in living cells.