Targeted cADDis: Live Cell cAMP Assays for Sub-cellular Domains
cADDis cAMP assays targeted to micro and nano domains of signaling.
- Detect localized signaling kinetics in live cells
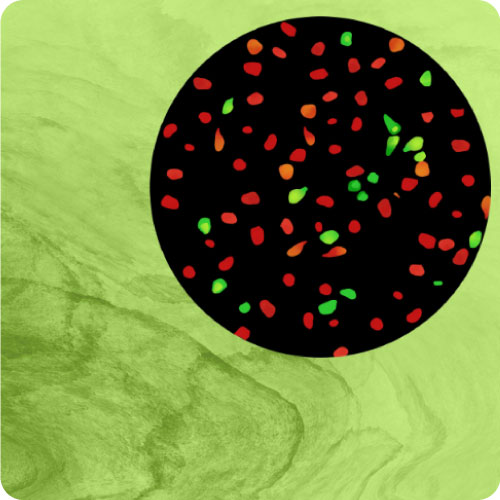
Cilia-targeted cAMP Assays
Our cilia-targeted cAMP assays were localized using a 5HT6 receptor. Green-only (D0201G) and ratiometric (D0211G) versions are available.
Publications using these tools:
- Paul G. DeCaen & Louise F. Kimura. Methods to Assess Neuronal Primary Cilia Electrochemical Signaling. Journal of Cellular Physiology. April 2025.
- S. Ansari, et al. Sonic Hedgehog activates prostaglandin signaling to stabilize primary cilium length. Journal of Cell Biology. June 2024.
- J. Hansen, et al. A cAMP signalosome in primary cilia drives gene expression and kidney cyst formation. EMBO Reports. June 2022.
- C. Wu, et al. Discovery of ciliary G protein-coupled receptors regulating pancreatic islet insulin and glucagon secretion. Genes & Development. August 2021.
- R. Sherpa et al. Sensory primary cilium is a responsive cAMP microdomain in renal epithelia. Scientific Reports. April 2019
-
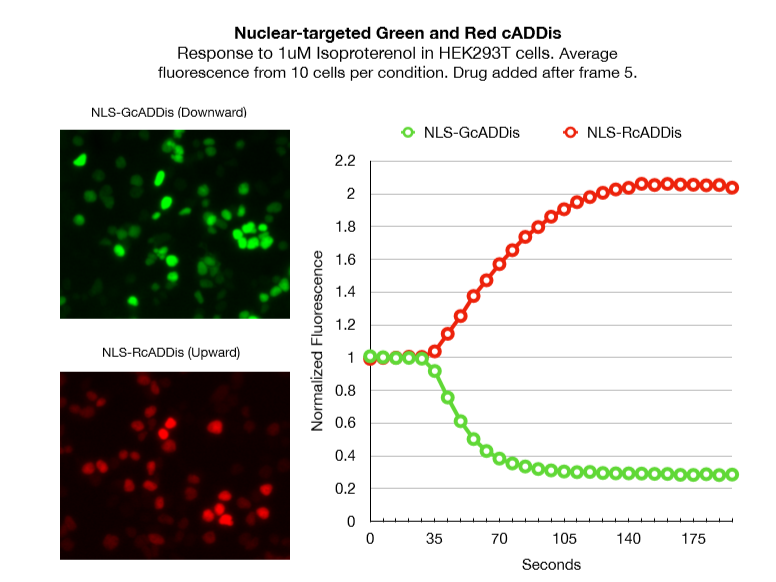
Nucleus-targeted cAMP Assays
cADDis sensors which have been targeted to the nucleus with an NLS motif. Red (U0221R) and Green (D0221G) NLS-targeted sensors are available. Both respond robustly to intracellular cAMP changes.
Example publications using these tools:
- S. Orfanos, et al. The differential effects of cAMP mobilizing agents on inhibition of TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix and growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts. Authorea. February 2025.
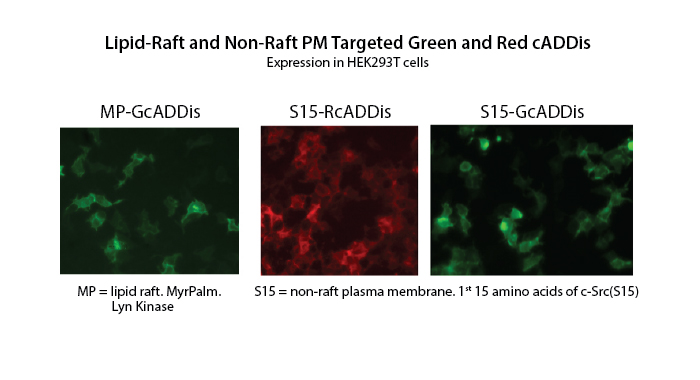
Membrane-targeted cAMP assays
Flag-tagged MyrPalm and S15 motifs target the cADDis sensor to the plasma membrane. Only green is available for fMP-targeted cADDis (D0231G), both red (U0241R) and green (D0241G) fluorescent fS15-targeted cADDis are available.
Example publications using these tools:
- R. Nassini, et al. Targeting the Schwann Cell EP2/cAMP Nanodomain to Block Pain but not Inflammation. bioRxiv. September 2024.
- ER McGlone, et al. Hepatocyte cholesterol content modulates glucagon receptor signaling. Molecular Metabolism. September 2022.
- N. Senese, et al. Antidepressants produce persistent Gαs associated signaling changes in lipid rafts following drug withdrawal. Molecular Pharmacology. May 2021.
AKAP-targeted cAMP Assays
There are many different AKAP Proteins that are localized to different regions of the cell. These AKAP Proteins bind the regulatory subunits of the PKA enzyme, but they often interact with adenyl cyclases, phosphodiesterases, and PKA substrates. This has led to the idea that they define “signalsomes” in the cell.
We have fused AKAP18 alpha, AKAP18 beta, AKAP1, AKAP79, AKAP 12, and smAKAP to our cADDis cAMP sensor. The videos below show these tools responding to isoproterenol in HEK293 cells.
Genetic targeting
Montana Molecular’s cADDis biosensor for cAMP measures the total level of cytoplasmic cAMP, providing robust, reproducible measurements of receptor activation and the waveform of the cellular response of the cell over minutes or hours (Hoare & Hughes, 2021). To measure cAMP signaling in specific signalsomes, new versions of cADDis were genetically targeted to effectively measure cAMP in particular subcellular compartments.
Subcellular cAMP signaling domains revealed with AKAP-targeted biosensors
Different neurotransmitters and drugs can produce very different effects on the same neuron, even though they all signal through an increase in cAMP. There are now biophysical measurements and models that help explain how this occurs.