cADDis: Live Cell Assays for cAMP
Detect Gs or Gi signaling with cADDis, our cAMP Assay
- Use cADDis to measure cAMP through Gs or Gi signaling in real time with a single sensor
- Plate reader or imaging system compatible
Measure cAMP through Gs or Gi Signaling in Real Time with a Single Sensor
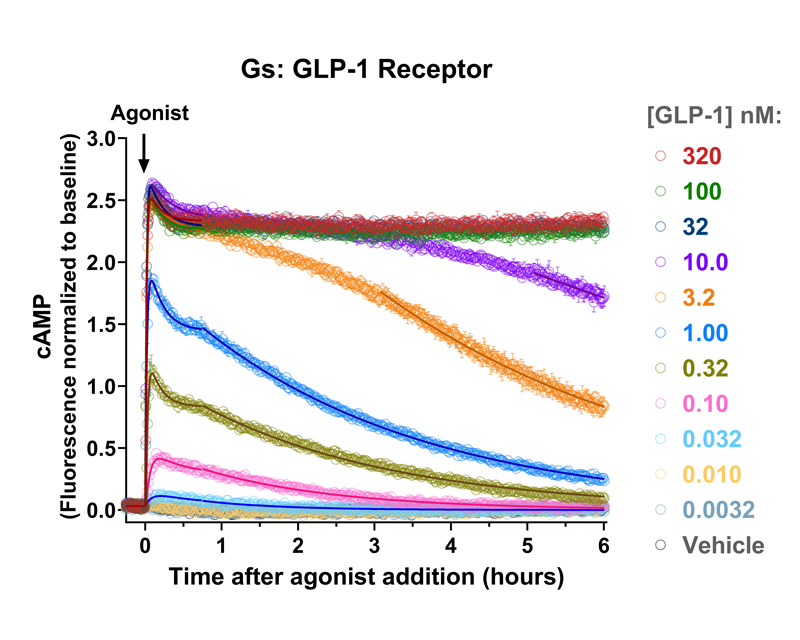
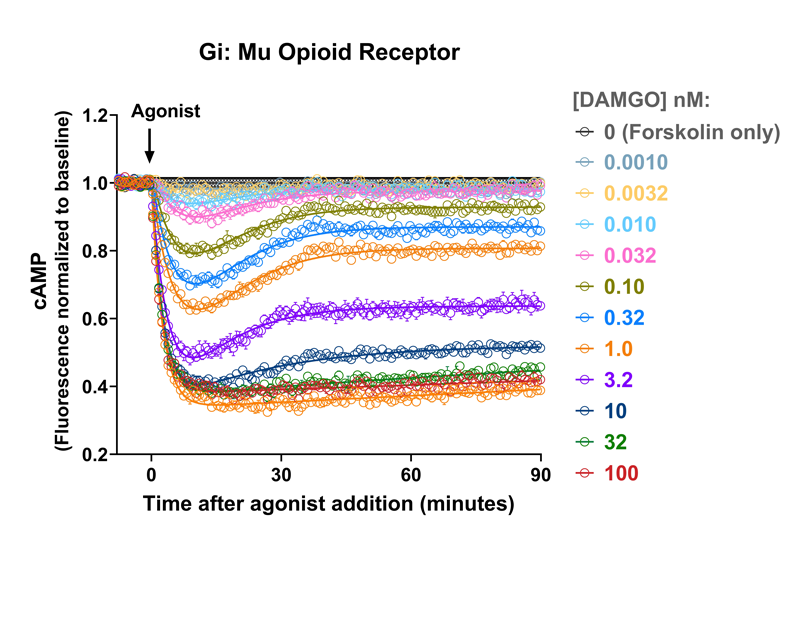
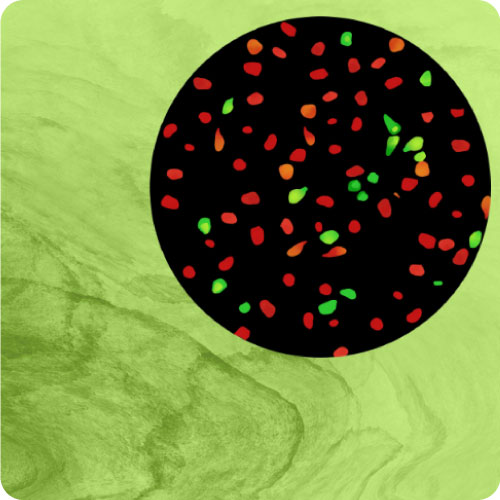
- Quantify kinetics of cyclic AMP signaling in living cells.
- Measure cAMP for many hours with minimal loss of sensor signal.
- Robust expression in practically any cell type.
Quantify cAMP Kinetics Precisely
- Changes over time reflect biological signaling mechanisms (rather than technical artifacts like sensor decay).
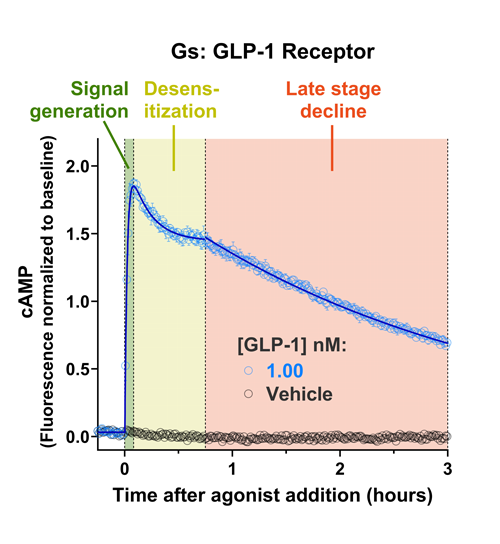
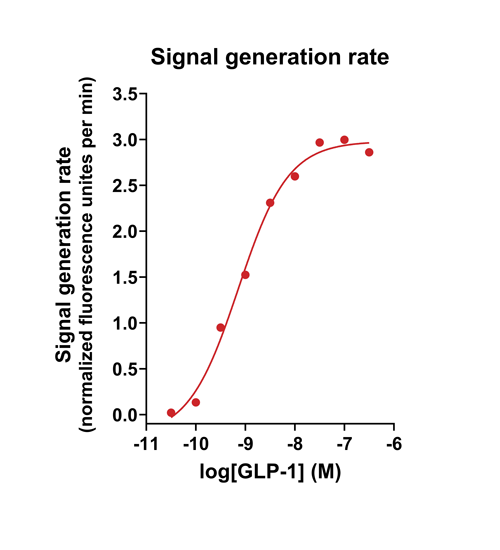
- Quantify signaling mechanisms by curve fitting time course data (see here for example report).
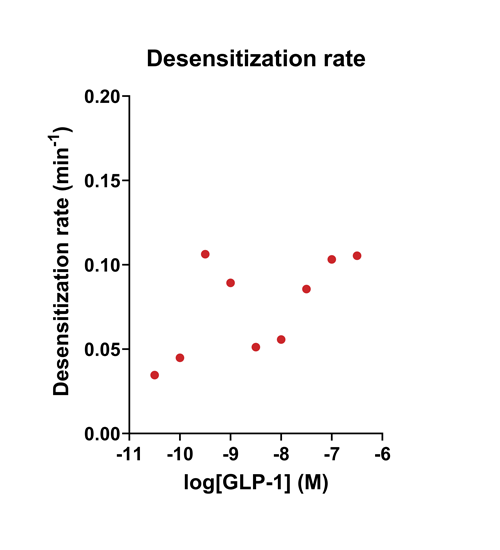
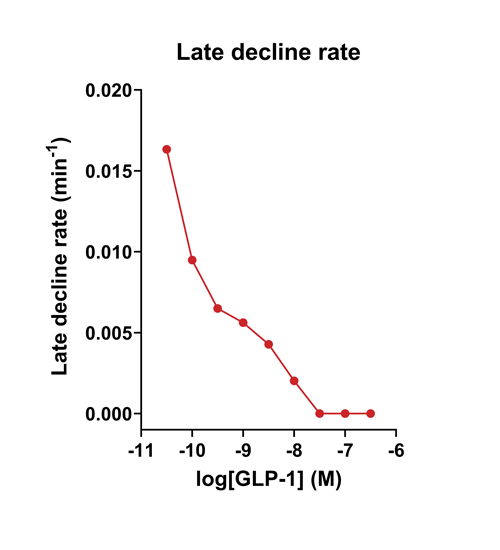
- In the example below we quantify the signal generation rate, signal decline resulting from desensitization, and late stage decline (likely resulting from peptide ligand degradation).
Your endpoint assays are missing important information. Measuring kinetics with our live-cell assays can reveal it.
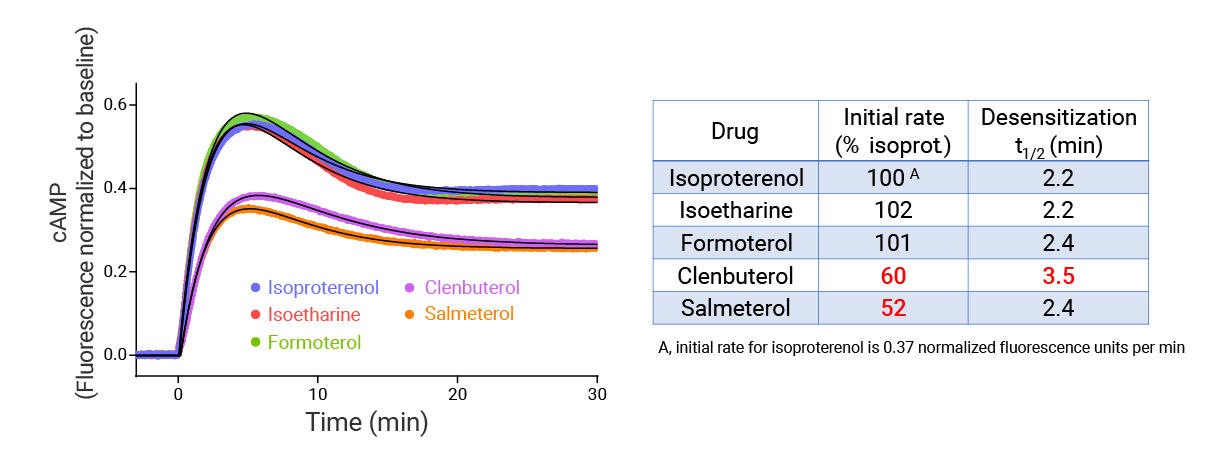
- Signaling dynamics of multiple drug compounds
- Different dynamics of cAMP generation by β2 adrenergic receptor agonists
- Clenbuterol and salbutamol generate cAMP more slowly and clenbuterol desensitizes receptor more slowly
A Robust & Versatile cAMP Assay Kit
- cADDis is a genetically-encoded fluorescent cyclic AMP assay that detects changes in cAMP in real time. Off the shelf kits include the cADDis sensor in BacMam, a BSL-1 viral vector for efficient delivery to most cell types. Purified BacMam, AAV, Lenti vectors by request.
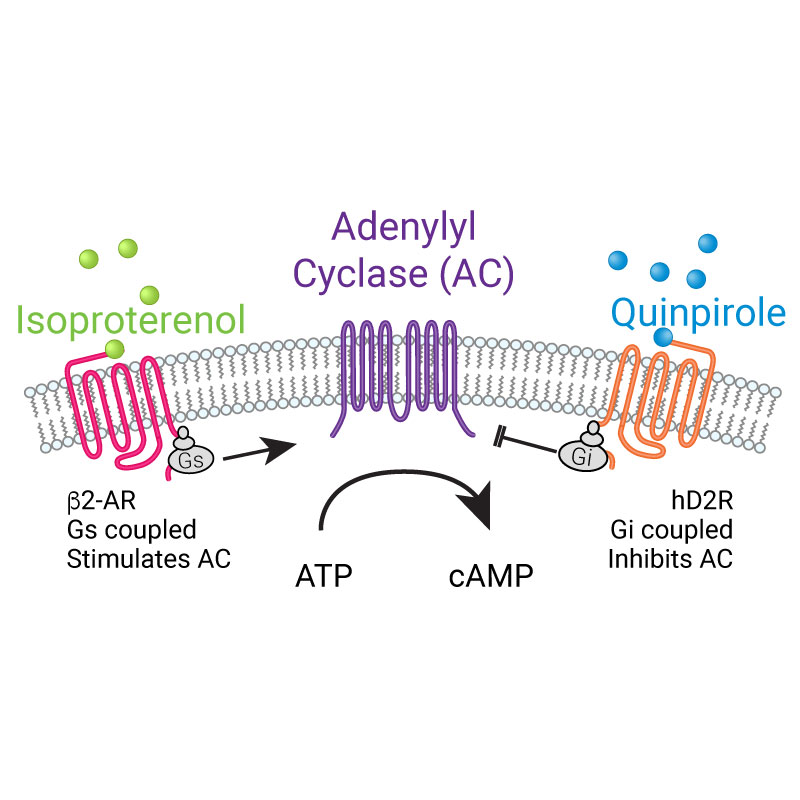
- Screen Gs or Gi-coupled GPCRs in living cells
- Target to microdomains or specific cells in mixed cultures
- Robust expression in practically any cell type
- Easily detectable on plate readers or imaging systems
- Controllable expression in BacMam viral vector
- High signal-to-noise ratio
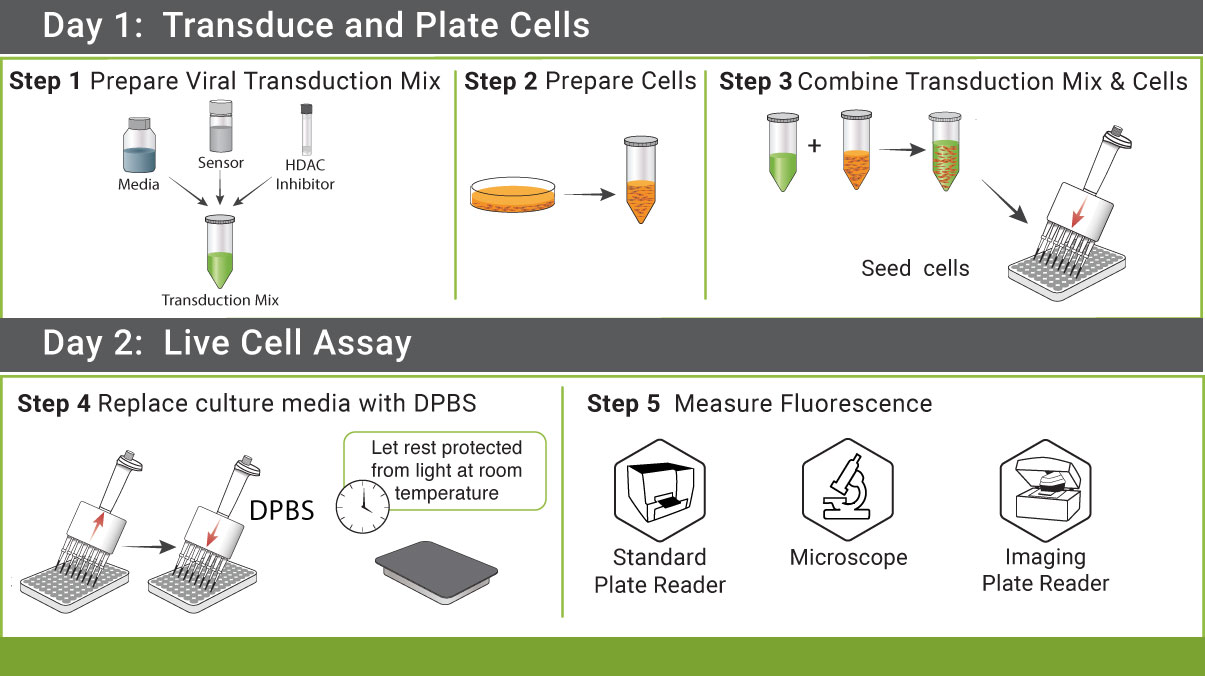
Simple Protocol
GPCR Assay Services
Go from hit to lead faster with compound profiling assays that capture GPCR signaling dynamics in living cells. Our unique biosensor-based discovery platform quantifies multiple signaling parameters in real time to enable decisions based on clinically-relevant data. Our fast turnaround time helps reduce the time to the clinic. We will perform experiments to advance your projects and programs, for example by optimizing assays, profiling compounds, exploring mechanisms and kinetically characterizing signaling dynamics.
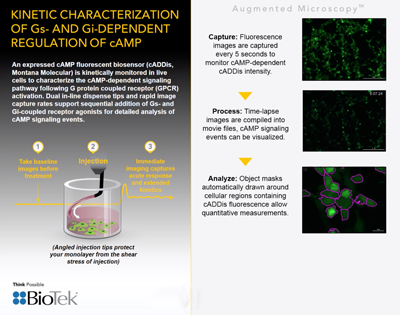
Check out this Live Cell Imaging video from BioTek Instruments: Kinetic Characterization of Gs- and Gi-dependent regulation of cAMP.
It’s a brief animated presentation demonstrating expression & kinetic monitoring of our fluorescent cADDis cAMP Assay in live cells.
Recent Publications
- S. Shi, et al. A high-affinity, cis-on photoswitchable beta blocker to optically control β2-adrenergic receptors in vitro and in vivo. Biochemical Pharmacology. June 2024.
- S. Ansari, et al. Sonic Hedgehog activates prostaglandin signaling to stabilize primary cilium length. Journal of Cell Biology. June 2024.
- A. Oqua, et al. Molecular mapping and functional validation of GLP-1R cholesterol binding sites in pancreatic beta cells. bioRxiv. June 2024.
- R. Schuck, et al. Cholesterol inhibits assembly and activation of the EphA2 receptor. bioRxiv. June 2024.
- X. Chen, et al. A PACAP-activated network for secretion requires coordination of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+ mobilization. Molecular Biology of the Cell. May 2024. (bioRxiv)
- L. Bridge, et al. Computational modelling of dynamic cAMP responses to GPCR agonists for exploration of GLP-1R ligand effects in pancreatic β-cells and neurons. Cellular Signaling, April 2024.
- R. Fagan, et al. Selective targeting of mu opioid receptors to primary cilia. Cell Reports. April 2024.
- G. Austin, et al. An inter-organelle contact between endosomal GLP-1R, ER VAP-B, and the mitochondrial AKAP SPHKAP triggers PKA-dependent MIC19 phosphorylation and β-cell mitochondrial remodelling. bioRxiv. April 2024.
- I. Cattani-Cavalieri, et al. Real-Time cAMP Dynamics in Live Cells Using the Fluorescent cAMP Difference Detector In Situ. Journal of Visualized Experiments. March 2024.
- B. Polacco, et al. Profiling the proximal proteome of the activated μ-opioid receptor. nature chemical biology. March 2024.
- P. Balraj, et al. Kisspeptin/KISS1R Signaling Modulates Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cell Migration. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. March 2024.
- J. Xu, et al. An evolutionarily conserved olfactory receptor is required for sex differences in blood pressure. Science Advances. March 2024 (bioRxiv)
- J. Alvarado et al. Transient cAMP production drives rapid and sustained spiking in brainstem parabrachial neurons to suppress feeding. Neuron. February 2024. (bioRxiv)
- H. Hamzeh, et al. Deciphering rapid cell signaling and control of cell motility by reverse opto-chemical engineering. bioRxiv. February 2024.
- N. Philip. Fatty acid metabolism promotes TRPV4 activity in lung microvascular endothelial cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. January 2024.
- L. Ripoll & M. von Zastrow. Spatial organization of adenylyl cyclase and its impact on dopamine signaling in neurons. bioRxiv. December 2023.
- T. Richardson, Y. Pettway, et al. Human Pseudoislet System for Synchronous Assessment of Fluorescent Biosensor Dynamics and Hormone Secretory Profiles. Journal of Visualized Experiments. November 2023.
- C. Hinds, et al. Abolishing β-arrestin recruitment is necessary for the full metabolic benefits of G protein-biased glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. October 2023.
- E. Blythe & M. von Zastrow. β-Arrestin-
independent endosomal cAMP signaling by a polypeptide hormone GPCR. Nature Chemical Biology. September 2023. - R. Matt, et al. Fingerprinting heterocellular β-adrenoceptor functional expression in the brain using agonist activity profiles. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. August 2023.
- Y. Kunioku, et al. Intracellular cAMP Signaling Pathway via Gs Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation in Rat Primary Cultured Trigeminal Ganglion Cells. Biomedicines. August 2023.
- K.M. Semesta, et al. The psychosis risk factor RBM12 encodes a novel repressor of GPCR/cAMP signal transduction. Journal of Biological Chemistry. August 2023.
- Y.J. Peng, et al. Hypoxia sensing requires H2S-dependent persulfidation of olfactory receptor 78. Science Advances. July 2023.
- S. Zhang, et al. Competition between stochastic neuropeptide signals calibrates the rate of satiation. bioRxiv. July 2023.
Posters: cADDis cAMP Assay
Measuring dynamic and real-time cAMP levels using cADDis, a live-cell indicator for Gs and Gi signaling
![]()
PDE Specificity Illuminated: Monitoring cGMP and cAMP Levels in Living Cells
![]()
GPCR Biology
Increase your understanding of drug effects and GPCR biology with bright fluorescent assays for Gs, Gi, and Gq signaling in living cells.