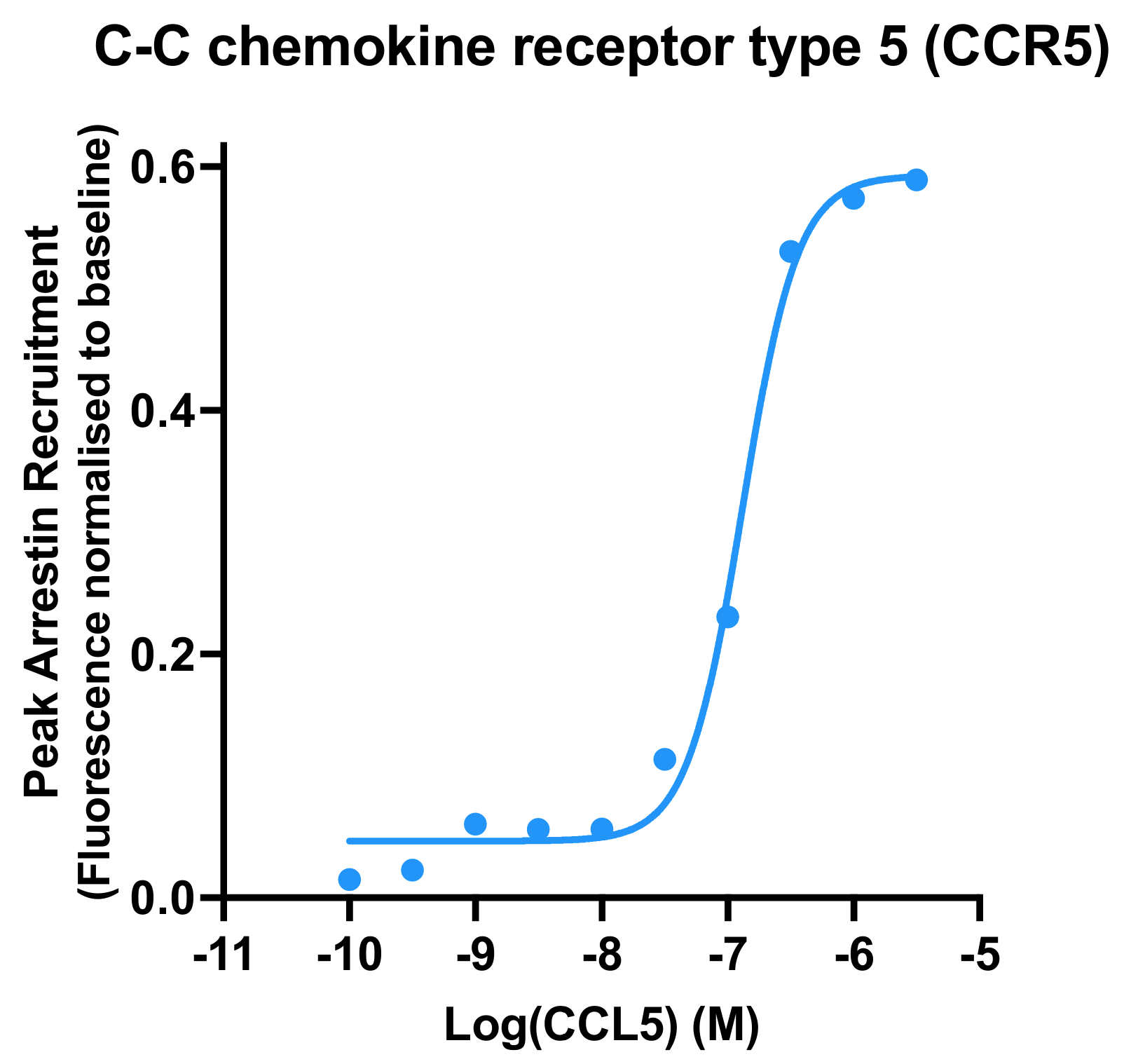
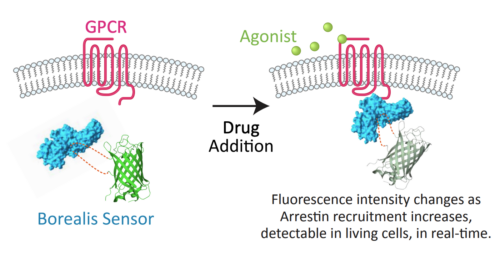
Borealis Arrestin – CCR5 (D2160G)
Price range: $1,095.00 through $2,095.00
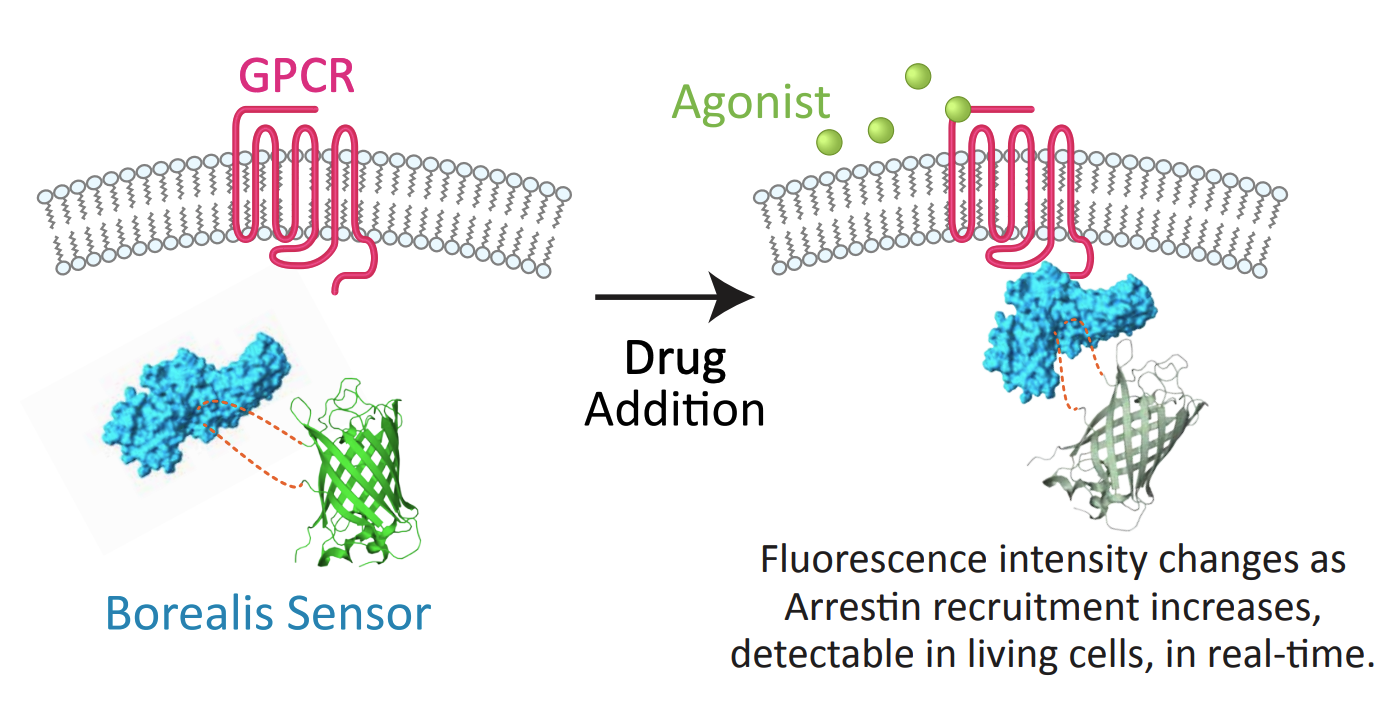
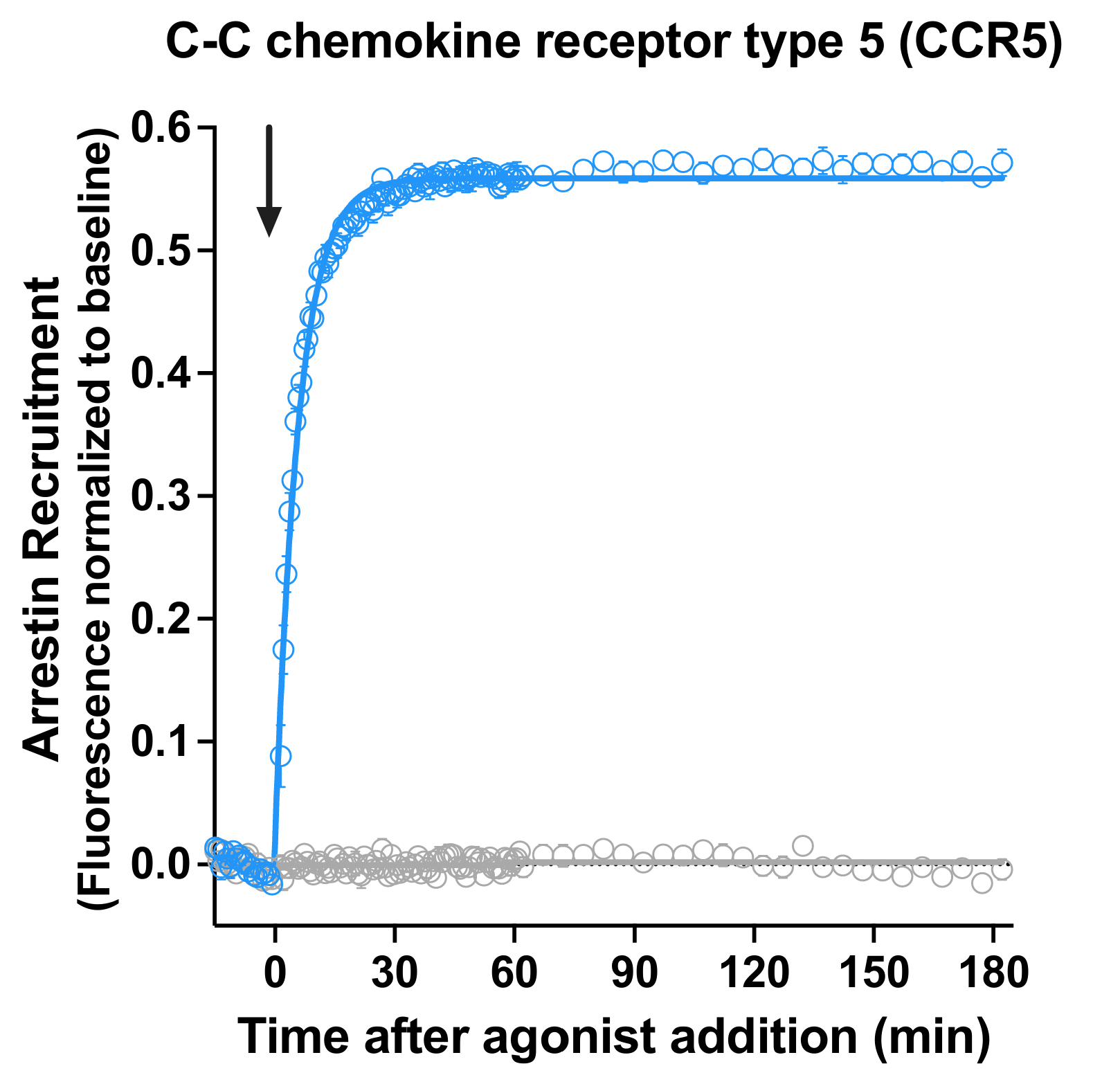
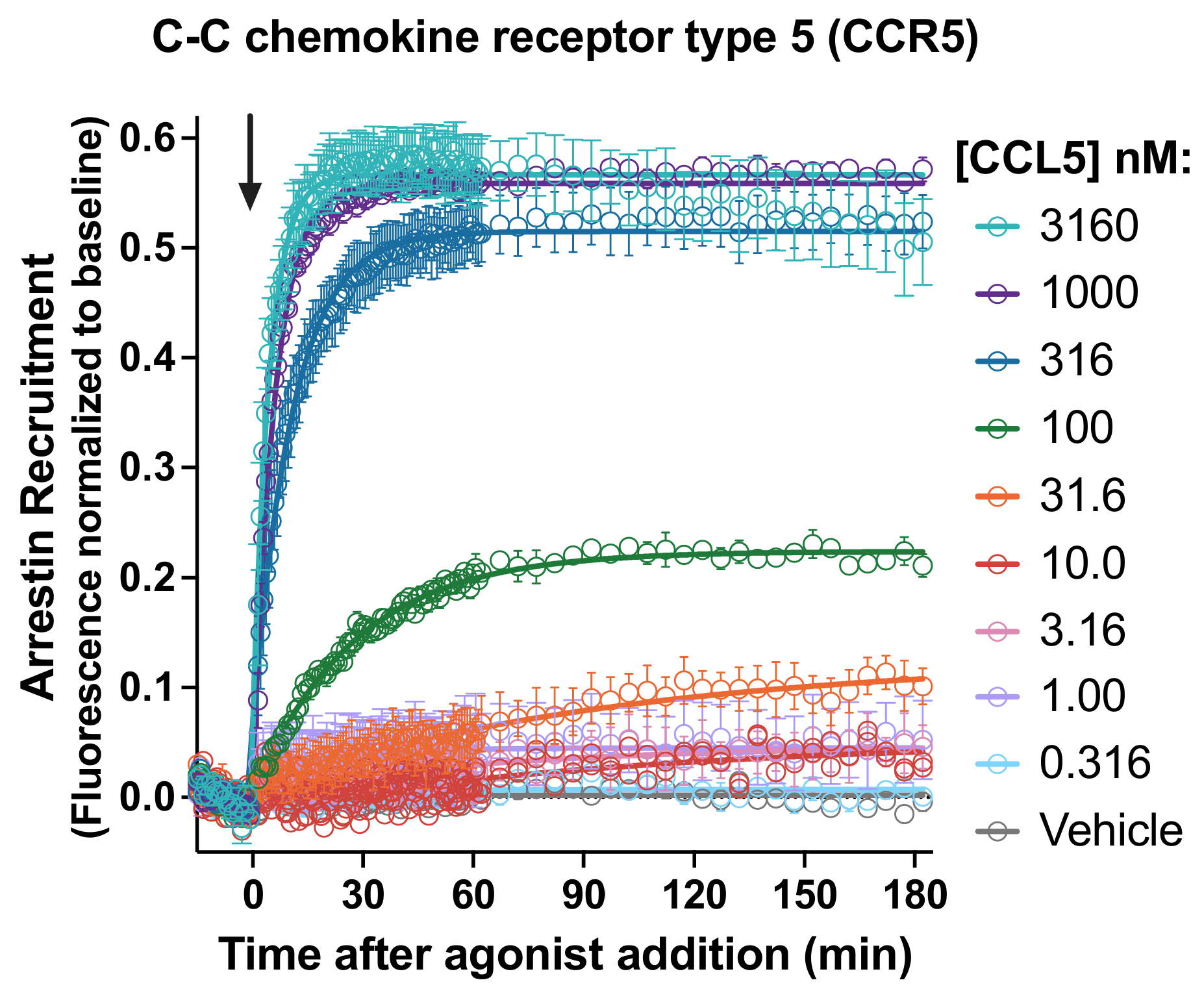
Borealis is a fluorescent biosensor assay for arrestin recruitment. This kit captures arrestin recruitment kinetics at the C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 5 (CCR5) in live cells.
A kinetic biosensor assay for arrestin recruitment converts conformational changes in arrestin-3 (β-arrestin-2) to changes in fluorescence intensity. This kit detects arrestin recruitment at the C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 5 (CCR5). The Borealis Arrestin Sensor, GRK5, and CCR5 are packaged in a BacMam viral vector for easy delivery to most cell types. Validated for use on fluorescence imaging systems and automated fluorescence plate readers. See the Borealis Arrestin Biosensors page for additional details.
Featured Posters:
- Using receptor kinetics to quantitatively measure agonist bias at G-protein coupled receptors
- Coloring β-arrestin signaling green, and G-protein signaling red, a new live cell assay for quantitatively measuring agonist bias at seven transmembrane domain receptors.
- Measuring biased agonism with a kinetic analysis platform for real time data from fluorescent biosensors
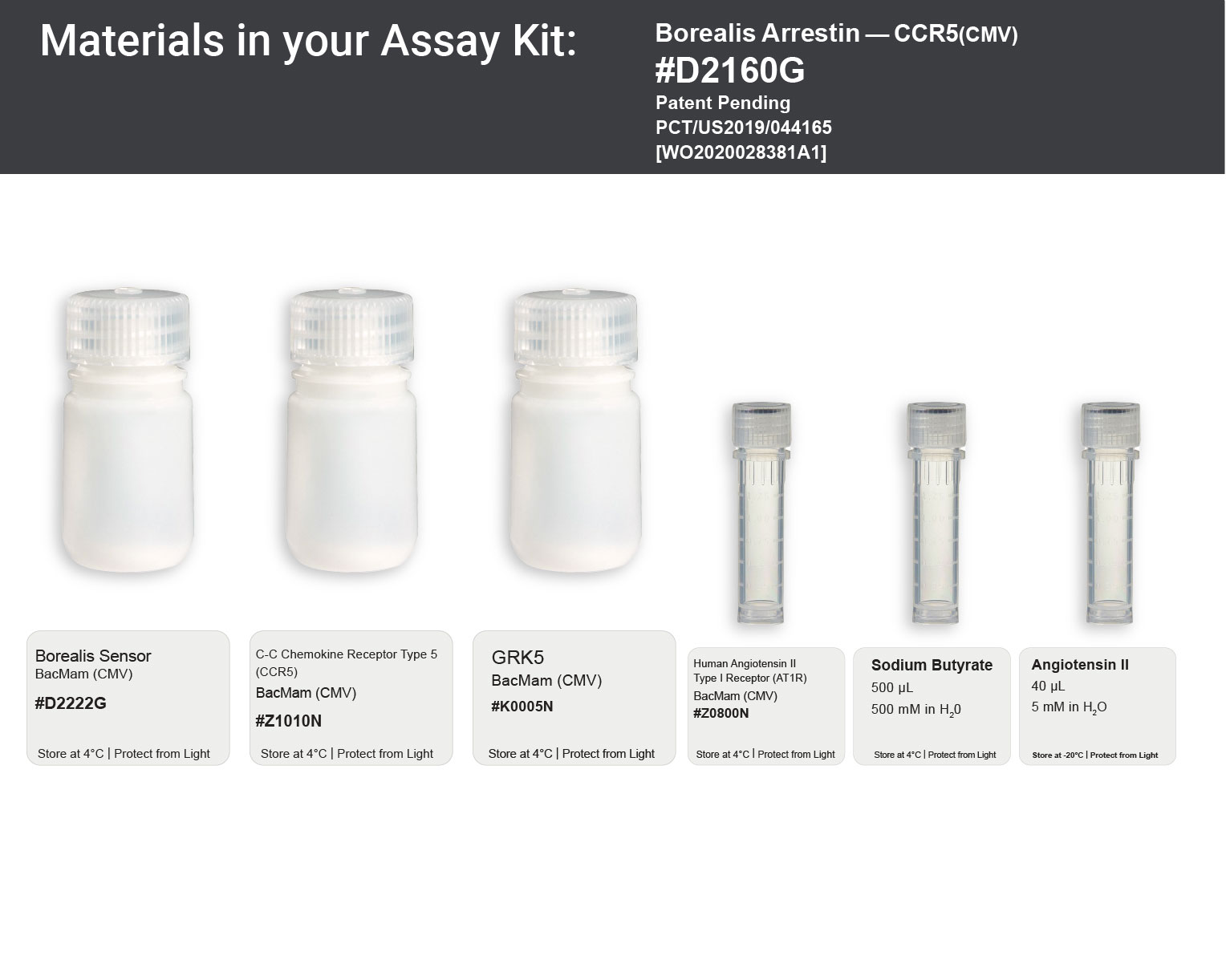
Materials in the Kit:
• Green Borealis Biosensor for arrestin, in BacMam
• C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 5 (CCR5), in BacMam
• Sodium Butyrate, 500mM in H2O
• Control Receptor: Angiotensin II-Type 1 (AT1R), in BacMam
• Control Agonist: Angiotensin II, 5mM in H2O
Additional information
| Protocol for Use | https://montanamolecular.com/beta-arrestin-assays/green-fluorescent-beta-arrestin-assays-protocol/ |
|---|---|
| Shipping | We strive for prompt delivery of each order, so we ship by FedEx 2-day service in lightweight, sturdy, and reusable/biodegradable packaging with an insulated cooler and moisture-resistant refrigerant gel packs. Shipping days are Mon-Wed so product does not sit in transit over the weekend. Web store ships to US & Canada only, contact sales for other locations. |
| MSDS | |
| Scientific Publications | |
| More Info | |
| Kit Volume | 10mL, 30mL, 60mL |
GPCR Assay References
Borealis Arrestin Assay References
- A. Ippolito, et al. Evidence that 5-HT2A receptor signalling efficacy and not biased agonism differentiates serotonergic psychedelic from non-psychedelic drugs. British Journal of Pharmacology. June 2025.
- E. Billard, et al. Pharmacological characterization of cannabidiol as a negative allosteric modulator of the 5-HT2A receptor. Cellular Signaling. January 2025.
- I. Davies, et al. Chronic GIPR agonism results in pancreatic islet GIPR functional desensitisation. Molecular Metabolism. January 2025.
- A. Ippolito, et al. Increased 5-HT2A receptor signalling efficacy differentiates serotonergic psychedelics from non-psychedelics. bioRxiv. June 2024.
- H. Schiff, et al. β-arrestin-biased proteinase-activated receptor-2 antagonist C781 limits allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. British Journal of Pharmacology. June 2022.
- S. Hoare, et al. Quantifying the Kinetics of Signaling and Arrestin Recruitment by Nervous System G-Protein Coupled Receptors. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. January 2022.
- S. Hoare, T. Hughes. Biosensor Assays for Measuring the Kinetics of G-Protein and Arrestin-Mediated Signaling in Live Cells. The Assay Guidance Manual. September 2021.
- S. Hoare, et al. Analyzing kinetic signaling data for G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature Scientific Reports. July 2020.
- S. Hoare, et al. A kinetic method for measuring agonist efficacy and ligand bias using high resolution biosensors and a kinetic data analysis framework. Nature Scientific Reports. Feb 2020.
cADDis cAMP Assay References
- Mark Lee & Keren Hilgendorf. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits adipogenesis through the cilia-dependent activation of ROCK2. Journal of Cell Science. September 2025.
- R. Nassini, et al. Targeting prostaglandin E2 receptor 2 in Schwann cells inhibits inflammatory pain but not inflammation. Nature Communications. September 2025.
- Tatsuru Togo. Disruption of the cell membrane triggers Ca2+ mobilization using P2Y receptors and subsequent cAMP synthesis in cells surrounding wounded MDCK cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. September 2025.
- C. Sturaro, et al. Activation of peripheral NOP receptors reduces periorbital mechanical allodynia evoked by CGRP in mice. British Journal of Pharmacology. August 2025.
- T. Cacciottolo, et al. Glucagon Receptor Deficiency Causes Early-Onset Hepatic Steatosis. Diabetes. August 2025.
- J. Chadwick, et al. Dietary-dependent sensitization of neuronal leptin signaling promotes neural repair after injury via cAMP and gene transcription. Neuron. August 2025.
- K. Berger, et al. Design of a peripherally biased NPSR1 antagonist for neuropeptide S induced inflammation. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. August 2025.
- C. Gao, et al. Semaglutide drives weight loss through cAMP-dependent mechanisms in GLP1R-expressing hindbrain neurons. bioRxiv. August 2025.
- Y. Manchanda, et al. Glycaemic and bodyweight effects of GIPR coding variation reflect differences in both surface expression and intrinsic functional impairment. medRxiv. August 2025.
- S. Orfanos, et al. The differential effects of cAMP mobilizing agents on TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix in human lung-derived fibroblasts: Insights into therapeutic targets for lung fibrosis. Research Square. August 2025.
- N. Saito, et al. Activation of G protein-coupled parathyroid hormone receptors in rat incisor odontoblasts promotes mineralization via cyclic adenosine monophosphate, not Ca2+ signalling: In vitro study. International Endodontic Journal. July 2025.
- M. Merz, et al. Downstream Signaling of Muscarinic M4 Receptors Is Regulated by Receptor Density and Cellular Environment. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives. May 2025.
- B. Wysolmerski, et al. Conformational biosensors delineate endosomal G protein regulation by GPCRs. bioRxiv. May 2025.
- Paul G. DeCaen & Louise F. Kimura. Methods to Assess Neuronal Primary Cilia Electrochemical Signaling. Journal of Cellular Physiology. April 2025.
- A. Oqua, et al. Molecular mapping and functional validation of GLP-1R cholesterol binding sites in pancreatic beta cells. eLife. April 2025. (bioRxiv)
- L. Coassolo, et al. Prohormone cleavage prediction uncovers a non-incretin anti-obesity peptide. Nature. March 2025.
- R. Schuck, et al. Cholesterol inhibits assembly and oncogenic activation of the EphA2 receptor. Nature Communications Biology. March 2025.
- E. Blythe, et al. Endocytosis sculpts distinct cAMP signal transduction by endogenously coexpressed GPCRs. bioRxiv preprint. February 2025.
- S. Orfanos, et al. The differential effects of cAMP mobilizing agents on inhibition of TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix and growth factor expression in human lung fibroblasts. Authorea. February 2025.
- A. Klein, et al. Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase 1 (AC1) and exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC) restores ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel activity after chronic opioid exposure. bioRxiv. February 2025.
- I. Davies, et al. Chronic GIPR agonism results in pancreatic islet GIPR functional desensitisation. Molecular Metabolism. January 2025.
- N. Patel, et al. Myosin VI drives arrestin-independent internalization and signaling of GPCRs. Nature Communications. December 2024.
- C. Bonner, et al. Metabolic State Determines Central and Peripheral Mechanisms of Liraglutide-Enhanced Insulin Secretion. Research Square. December 2024.
- M. Kimura, et al. Intracellular cAMP signaling-induced Ca2+ influx mediated by calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) in human odontoblasts. European Journal of Physiology. November 2024.
- A. Ali, et al. Comparative Effects of GLP-1 and GLP-2 on Beta-Cell Function, Glucose Homeostasis and Appetite Regulation. Biomolecules. November 2024.
- A. Hamilton, et al. Nicotinic signaling stimulates glucagon secretion in mouse and human pancreatic α-cells. Diabetes. October 2024.
- LE Eid, et al. In vivo functional profiling and structural characterisation of the human Glp1r A316T variant. bioRxiv. October 2024.
DAG Assay References
- E. Lukovic, et al. Design and Evaluation of Novel Ginger 6-Shogaol-Inspired Phospholipase C Inhibitors to Enhance β-Agonist-Induced Relaxation in Human Airway Smooth Muscle. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. June 2025.
- E. Billard, et al. Pharmacological characterization of cannabidiol as a negative allosteric modulator of the 5-HT2A receptor. Cellular Signaling. January 2025.
- X. Chen, et al. Roles for PKC signaling in chromaffin cell exocytosis. Biophysical Journal. December 2024.
- A. Hamilton, et al. Nicotinic signaling stimulates glucagon secretion in mouse and human pancreatic α-cells. Diabetes. October 2024.
- X. Chen, et al. A PACAP-activated network for secretion requires coordination of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+ mobilization. Molecular Biology of the Cell. May 2024. (bioRxiv)
- S. Datta, et al. APOL1-mediated monovalent cation transport contributes to APOL1-mediated podocytopathy in kidney disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. January 2024. (Supplemental Data)
- Z. Miller, et al. Lidocaine induces apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through activation of bitter taste receptor T2R14. Cell Reports. November 2023. (bioRxiv)
- N. Zaïmia, et al. GLP-1 and GIP receptors signal through distinct β-arrestin 2-dependent pathways to regulate pancreatic β cell function. Cell Reports. October 2023.
- G. Sanchez, et al. Coincident Regulation of PLCβ Signaling by Gq-Coupled and μ-Opioid Receptors Opposes Opioid-Mediated Antinociception. Molecular Pharmacology. December 2022.
- Z. Miller, et al. Lidocaine Induces Apoptosis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Through Activation of Bitter Taste Receptor T2R14. bioRxiv. November 2022.
- M. Doepner, et al. Endogenous DOPA inhibits melanoma through suppression of CHRM1 signaling. Science Advances. September 2022.
PIP2 Assay References
- V. Chandar, et al. Intercellular contact is sufficient to drive Fibroblast to Myofibroblast transitions. arXiv. March 2025.
- L. Brueggemann, et al. Structural Determinants of Kv7.5 Potassium Channels that Confer Changes in Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Biphosphate (PIP2) Affinity and Signaling Sensitivity in Smooth Muscle Cells. Molecular Pharmacology. March 2020.
- L.Liu, et al. Gαq sensitizes TRPM8 to inhibition by PI(4,5)P2 depletion upon receptor activation. J.Neurosci. May 2019.
- , and Teaching an Old Drug New Tricks: Agonism, Antagonism, and Biased Signaling of Pilocarpine through M3 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Molecular Pharmacology Nov. 2018
GECO Calcium Assay References
- X. Chen, et al. Roles for PKC signaling in chromaffin cell exocytosis. Biophysical Journal. December 2024.
- X. Chen, et al. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of the host TRPC4 channel attenuates Zika virus infection. EMBO Molecular Medicine. July 2024.
- X. Chen, et al. A PACAP-activated network for secretion requires coordination of Ca2+ influx and Ca2+ mobilization. Molecular Biology of the Cell. May 2024. (bioRxiv)
- C. Amos, et al. Membrane lipids couple synaptotagmin to SNARE-mediated granule fusion in insulin-secreting cells. Molecular Biology of the Cell. December 2023.
- J. Wu, et al. Interaction Between HCN and Slack Channels Regulates mPFC Pyramidal Cell Excitability and Working Memory. bioRxiv. March 2023.
- M. Thomas, et al. Optically activated, customizable, excitable cells. PLOS One. December 2020.
- L. Liu, et al. Diacylglycerol kinases regulate TRPV1 channel activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry. April 2020.
- S. Hoare, et al. A kinetic method for measuring agonist efficacy and ligand bias using high resolution biosensors and a kinetic data analysis framework. Nature Scientific Reports Feb 2020.
- K. Harlen, et al. Live-Cell Assays for Cell Stress Responses Reveal New Patterns of Cell Signaling Caused by Mutations in Rhodopsin, α-Synuclein and TDP-43 Front. Cell. Neurosci.,December 2019