Cell Stress Assays
Detect Stress Responses in Living Cells
Our cell stress assays produce a bright green fluorescent protein when the cell endures endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress or undergoes the unfolded protein response (UPR). This robust assay can be detected on standard fluorescence plate readers or imaging systems.
Fluorescent Tools to Monitor Cell Stress & Toxicity
Bright fluorescent assays to detect response and reversal of chemical or genetic ER stress response and UPR. Don’t settle for counting dead cells…instead, take a closer look at the biology.
- Discover a bright fluorescent assay for detecting ER-mediated stress and the UPR
- Neurotoxicity assay in iPSC-derived neurons or cardiomyocytes
- Simultaneous readouts of disrupted Ca2+signals in stressed cells
- Assay reversibility follows stress reversal
- Reveal disrupted signals that underlie neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration.
New IRE1-XBP1 ER Stress Assay
- Detect cell stress by way of the IRE1-XBP1 arm of the UPR
- Cells produce bright green fluorescence when undergoing stress and constitutively express a red FP for ratiometric analysis or to monitor cell health
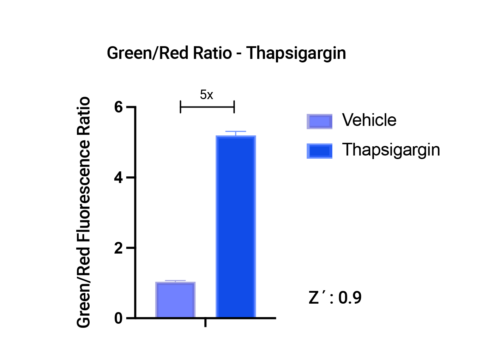
- Measure either green fluorescence or take the green/red fluorescence ratio, both with high Z’
- Green and red fluorescence is targeted to the nucleus to simplify image analysis using microscopy or high-content imaging systems
- This is an update to the ratiometric cell stress assay (U0901G), using the bright, rapidly folding Montana Paintbrush RFP for more robust detection on plate readers
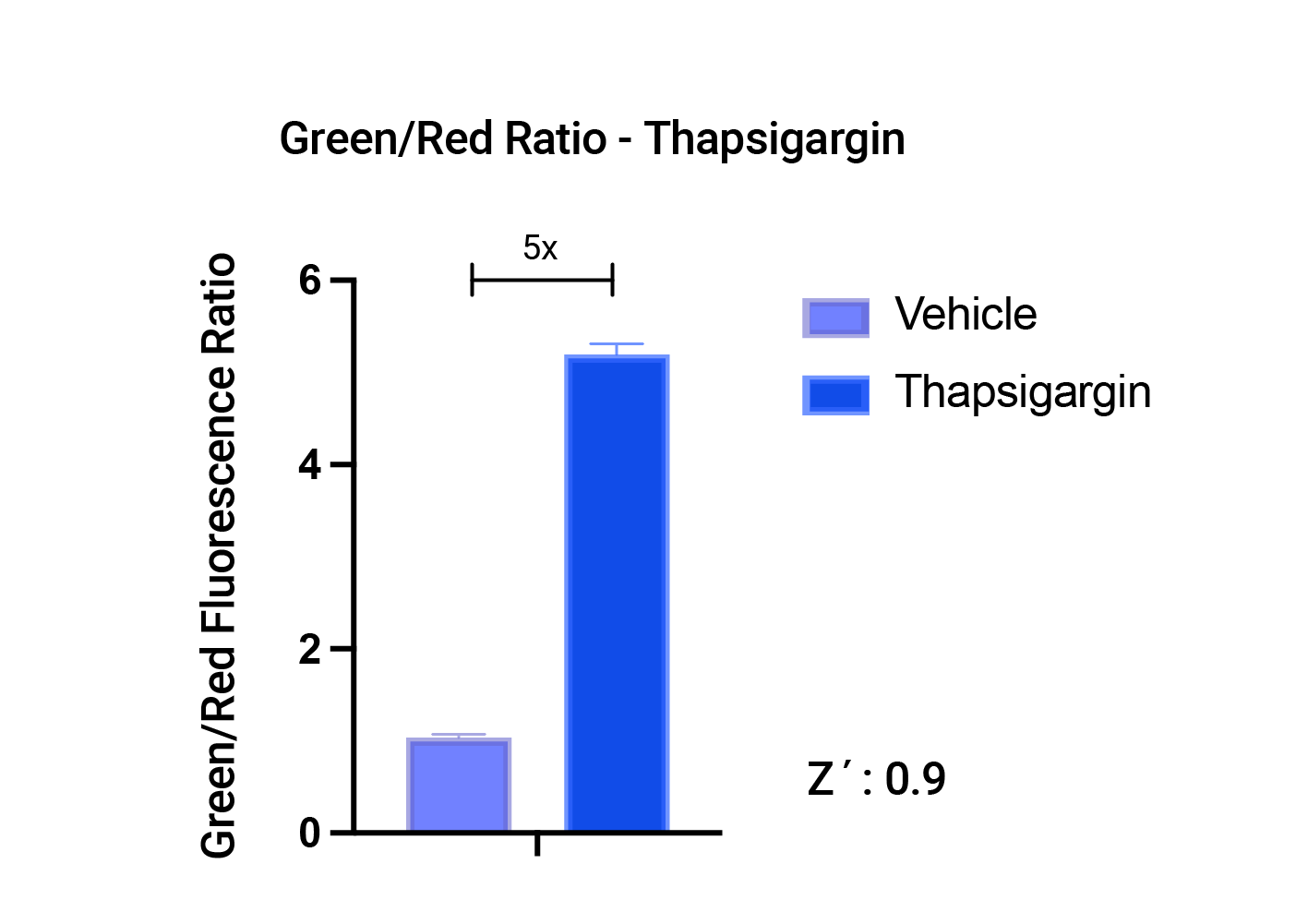
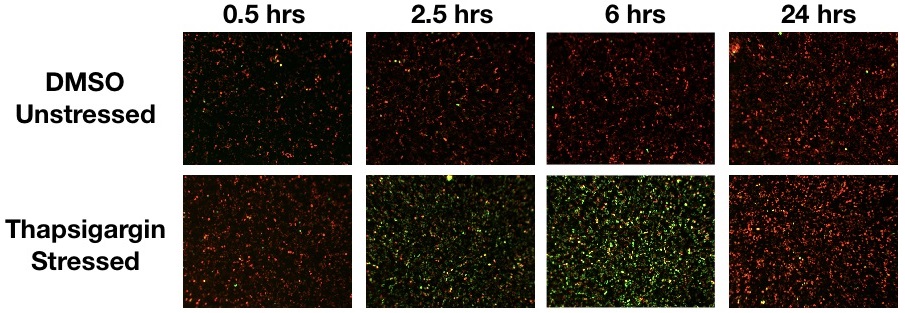
Stress response in HEK293 cells in response to Thapsigargin treatment. Stress measured with #U0921G using the Green/Red fluorescence ratio.
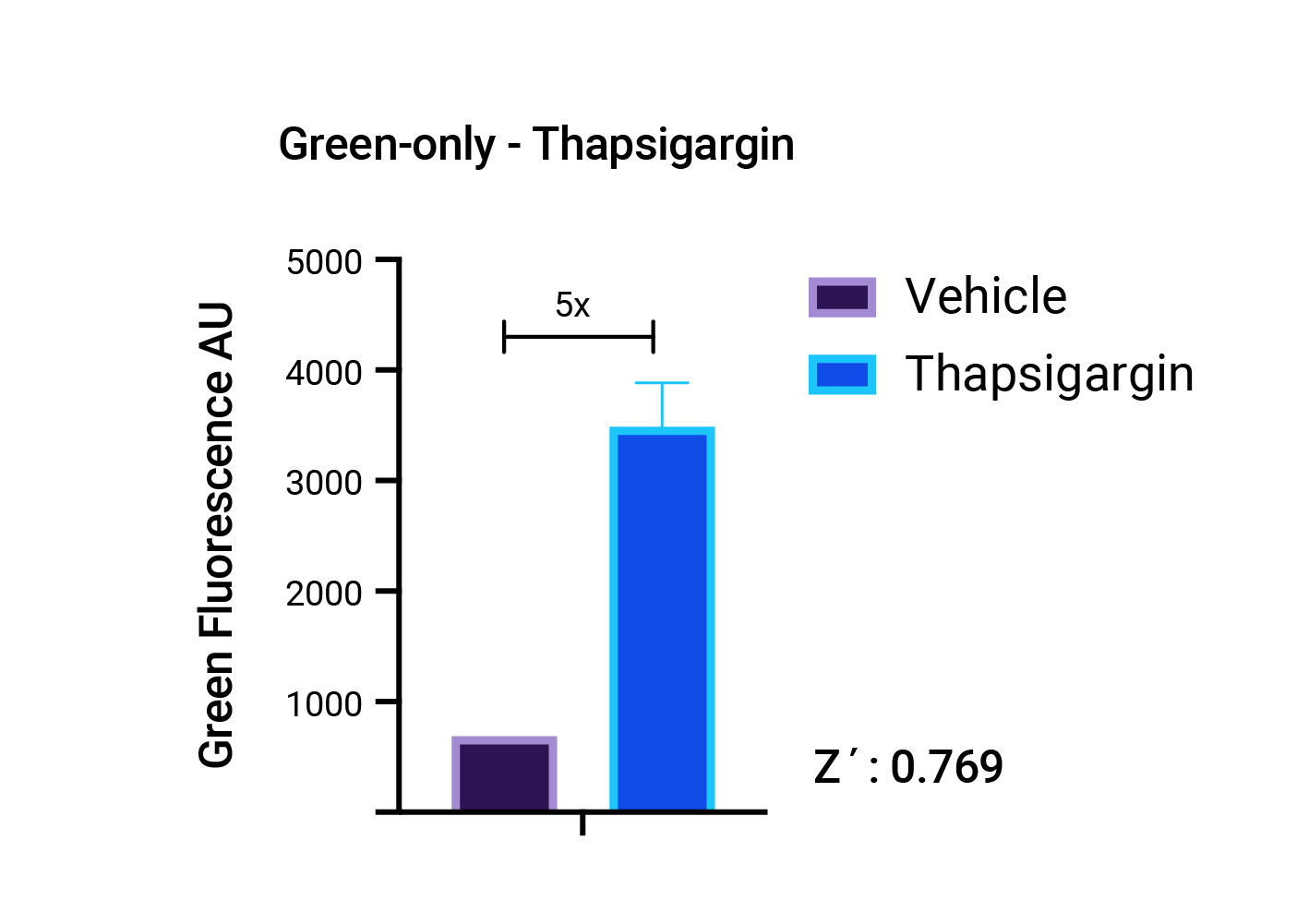
Stress response in HEK293 cells in response to Thapsigargin treatment. Stress measured with #U0921G using the Green fluorescence only.
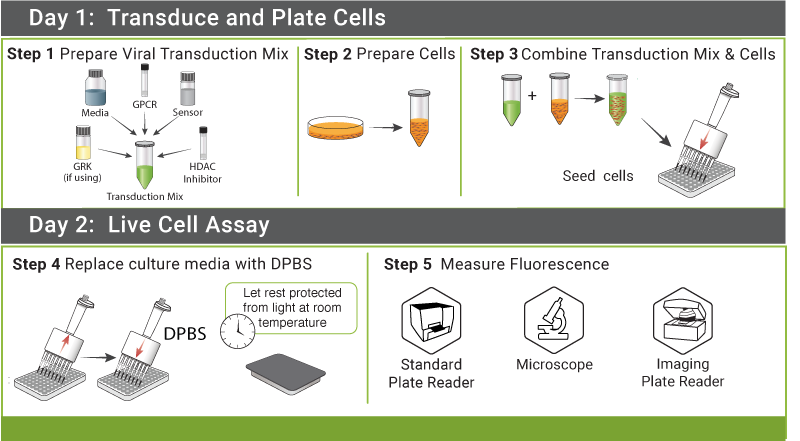
Simple Protocol
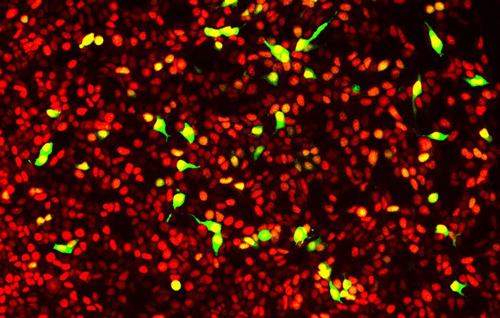
Nuclear Targeted
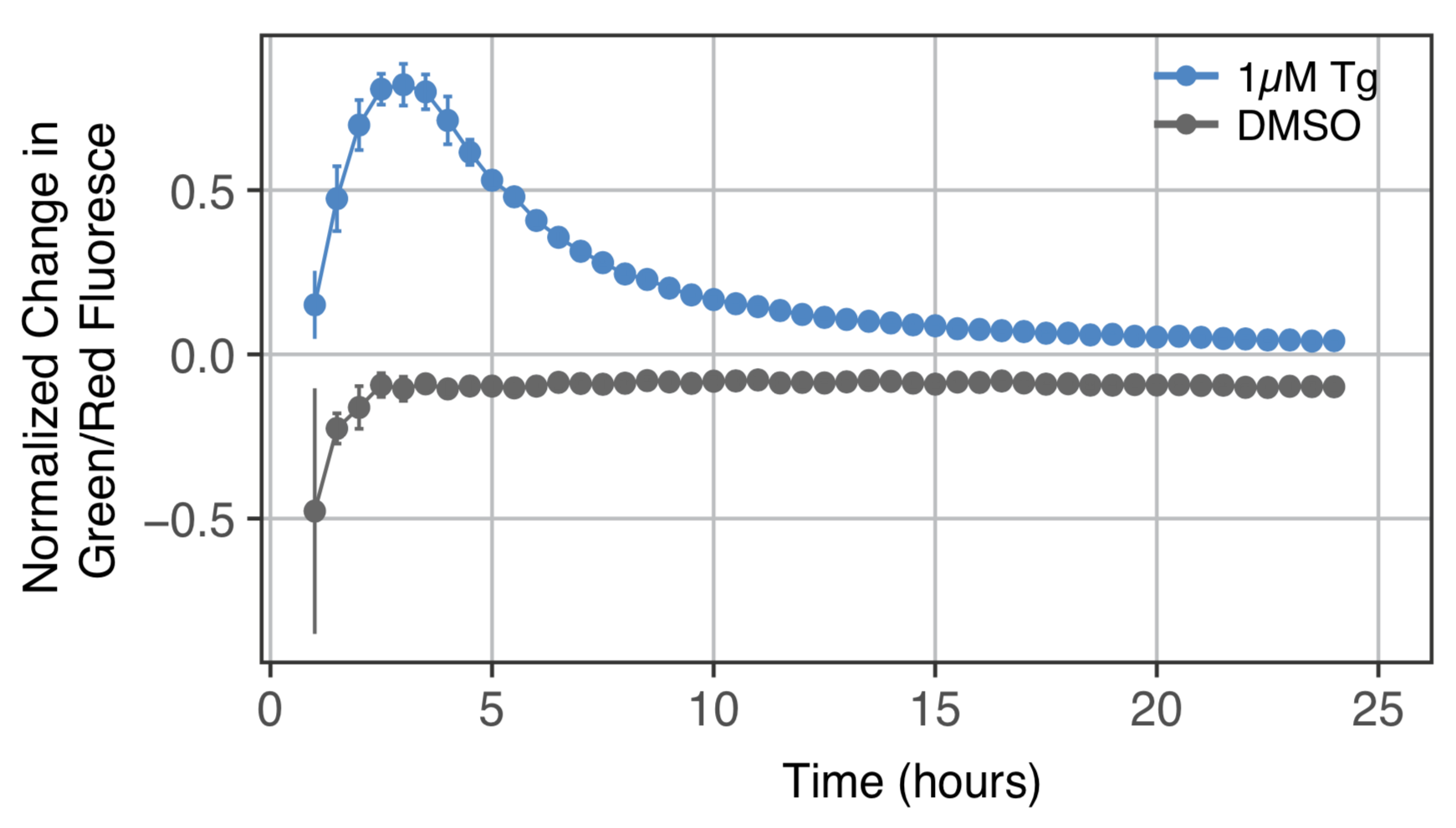
Detecting Chemical Stress
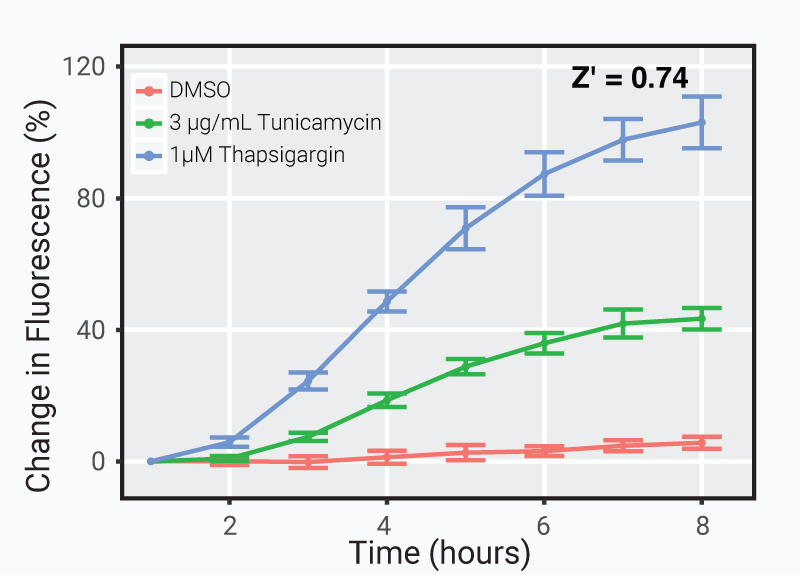
Discriminate between toxic compounds in less than 8 hours.
Cells transduced with 25 μL of green cell stress sensor and activated with either thapsigargin or tunicamycin. The plot displays the percent change in fluorescence over time compared to 1 hour after addition of either drug or DMSO control.
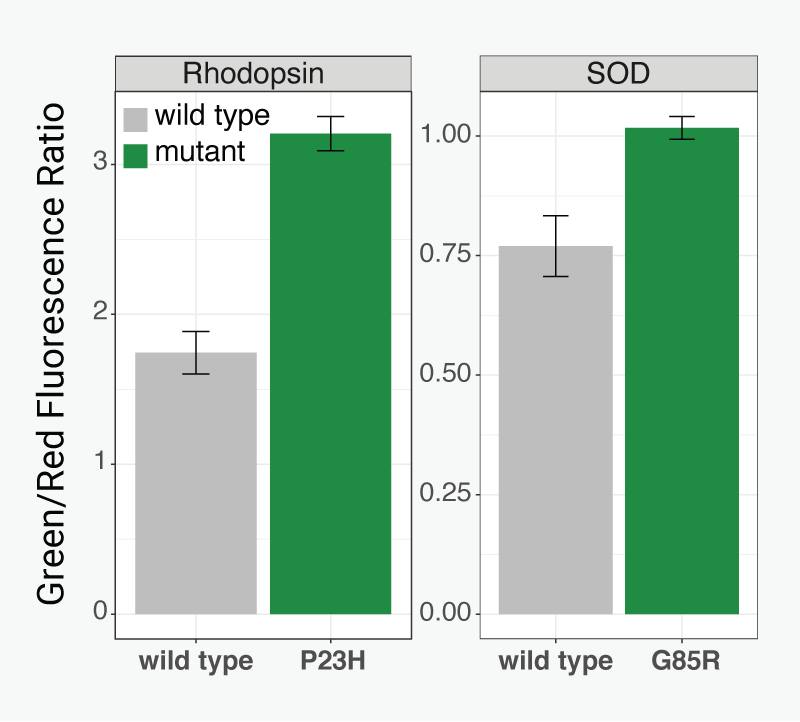
Detecting Genetic Stress
Reach for a better understanding of neurodegeneration with a robust and reversible assay that indicates the stress pathway involved in protein misfolding and aggregation. Cells expressing Rhodopsin P23H mutation in Retinitis Pigmentosa, and SOD G85R mutation in ALS clearly indicated after just 18 hours.
Two-color Ratiometric Stress Assay
Two-color ratiometric stress biosensor: This version of the assay is designed for ratiometric measurements using the green fluorescent sensor and a constitutively expressed red fluorescent protein. Red and green fluorescent signals are both localized to the nucleus. Red fluorescence indicates all cells expressing the sensor, and green fluorescence indicates cells undergoing the stress response.
Detecting Stress Reversal
A red fluorescent nucleus turns green when the cells become stressed and back to red when cells recover, making it easy to identify therapeutic compounds that reverse ER-mediated stress and the UPR.
The cell stress assay is packaged in BacMam, a BSL-1 viral vector for efficient expression in a wide variety of cell types including primary cells, standard cell lines, and iPSC derived cells. In the videos below we show how the cell stress assay responds to stress and toxicity in iPSC neurons and cardiomyocytes.
Stress and toxicity assay in iPSC derived neurons
Stress and toxicity assay in iPSC cardiomyocytes
Intro Video
- Meet the scientists who developed the Cell Stress Assay
- Learn how the Cell Stress Assay can be a critical tool in your research
- Identify compounds that reverse cell stress
Recent Posters and Publications
New Fluorescent Tools for Monitoring Cell Stress and Toxicity
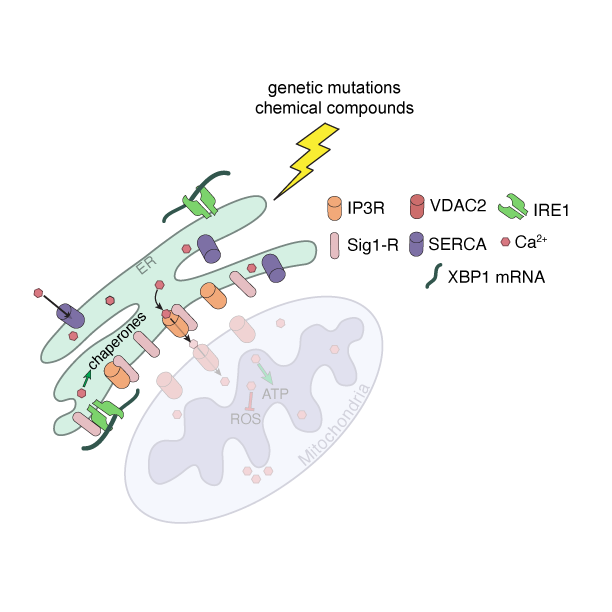
The cell stress sensor is a genetically-encoded fluorescent biosensor that produces very bright fluorescence when the cell endures endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress or undergoes the unfolded protein response (UPR). A broad host of both chemical compounds and genetic mutations can induce ER stress. The UPR is one of the major stress pathways within the cell, which allows the stress sensor to detect a wide range of stress inducing stimuli, some whose primary target is not the ER.
- C. Byrnes, et al. 1-Deoxysphingolipids Require Very-Long-Chain Ceramide Synthesis to Induce ER Stress and Neurotoxicity. bioRxiv. December 2025.
- D. Wang, et al. Azoramide attenuates thapsigargin-induced ER stress and cell death in human SH-SY5Y cells via maintaining intracellular calcium homeostasis. European Journal of Pharmacology. November 2025.
- M. Pathak & A. Spradling. Mouse germline cysts contain a fusome that mediates oocyte development. bioRxiv. September 2025.
- G. Roy, et al. VDAC1 is a target for pharmacologically induced insulin hypersecretion in β cells. Cell Reports. June 2025.
- N. Shimizu, et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Apoptosis of Cancer Cells Induced by a Kinase-Responsive Peptide Amphiphile. Chemistry Europe. January 2025.
- G. Roy, et al. Target deconvolution of an insulin hypersecretion-inducer acting through VDAC1 with a distinct transcriptomic signature in beta-cells. bioRxiv. December 2024.
- B. Dhayalan, et al. Synthetic Studies of the Mutant Proinsulin Syndrome Demonstrate Correlation Between Folding Efficiency and Age of Diabetes Onset. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics. November 2024.
- N. Borkar, et al. Nicotine-induced ER Stress and ASM Cell Proliferation is Mediated by α7nAChR and Chaperones-RIC-3 and TMEM35. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. September 2024.
- M. Ho, et al. Molecular mechanisms involved in alcohol craving, IRF3, and endoplasmic reticulum stress: a multi-omics study. Nature Translational Psychiatry. March 2024.
- L. Scheherazade Milane. Combination Organelle Mitochondrial Endoplasmic Reticulum Therapy (COMET) for Multidrug Resistant Breast Cancer. Journal of Controlled Release. October 2023.
- S. Sanchez-Martinez, et al. Labile assembly of a tardigrade protein induces biostasis. bioRxiv. July 2023.
- N. Mohammed, et al. Mechanisms of cell death induced by hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) involves apoptosis, autophagy, and ER stress. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology. June 2023.
- K. Harlen, et al. Live-Cell Assays for Cell Stress Responses Reveal New Patterns of Cell Signaling Caused by Mutations in Rhodopsin, α-Synuclein and TDP-43 Frontiers Cellular Neuroscience. December 2019.
- K. Harlen, et al. Live-cell biosensors reveal novel insight into neurotoxic and cardiotoxic compound mediated cellular stress response. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. October 2019.